We should avoid the term “fluid overload”, Critical Care
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 10 abril 2025

Extracorporeal Ultrafiltration for Fluid Overload in Heart Failure: Current Status and Prospects for Further Research - ScienceDirect

Fluid management in the critically ill - ScienceDirect
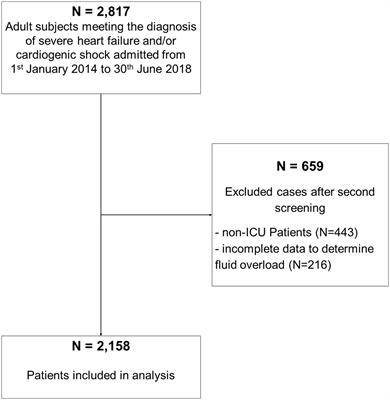
Frontiers Fluid overload and mortality in critically ill patients with severe heart failure and cardiogenic shock–An observational cohort study

Association between the volume of fluid resuscitation and mortality modified by disease severity in patients with sepsis in ICU: a retrospective cohort study

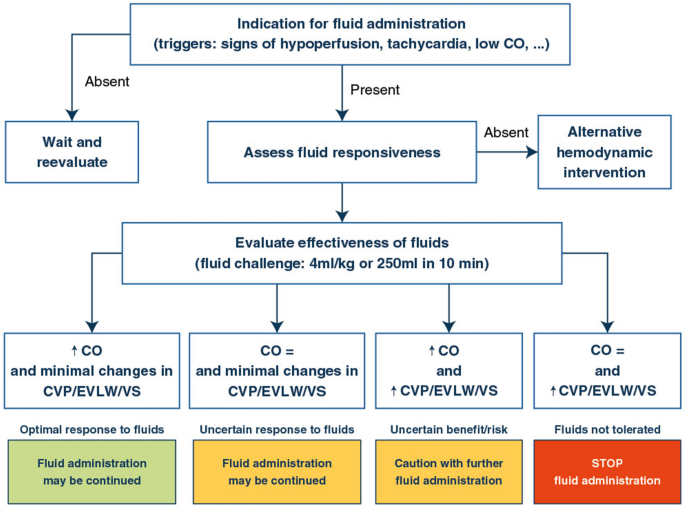
Selecting IV fluids to manage fluid loss in critically ill patients
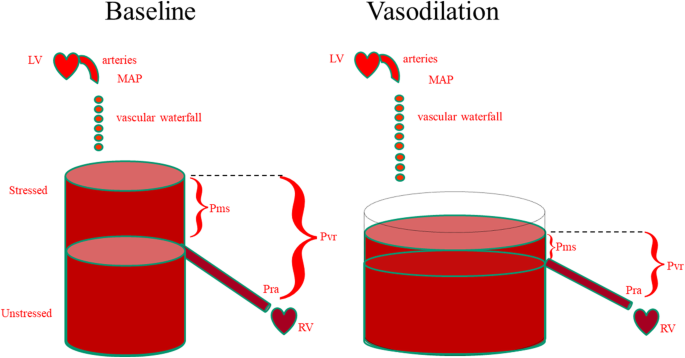
How can assessing hemodynamics help to assess volume status?
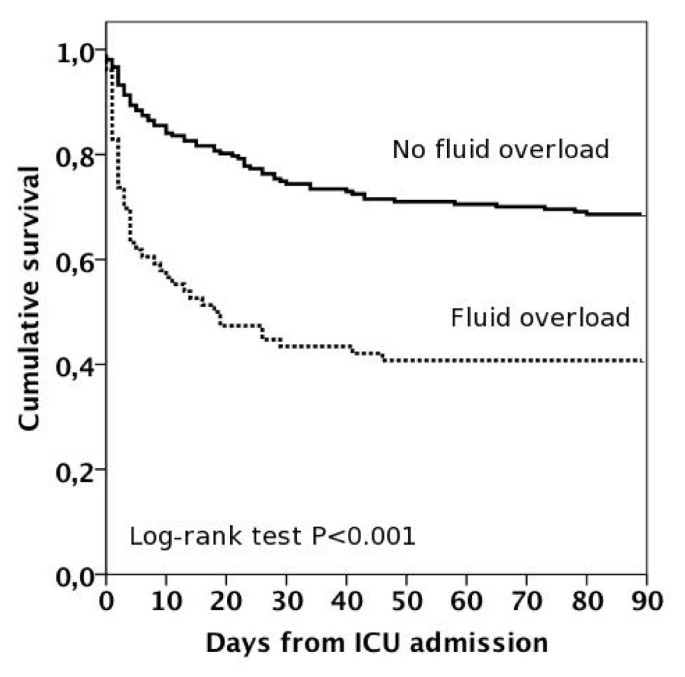
Fluid overload is associated with an increased risk for 90-day mortality in critically ill patients with renal replacement therapy: data from the prospective FINNAKI study, Critical Care
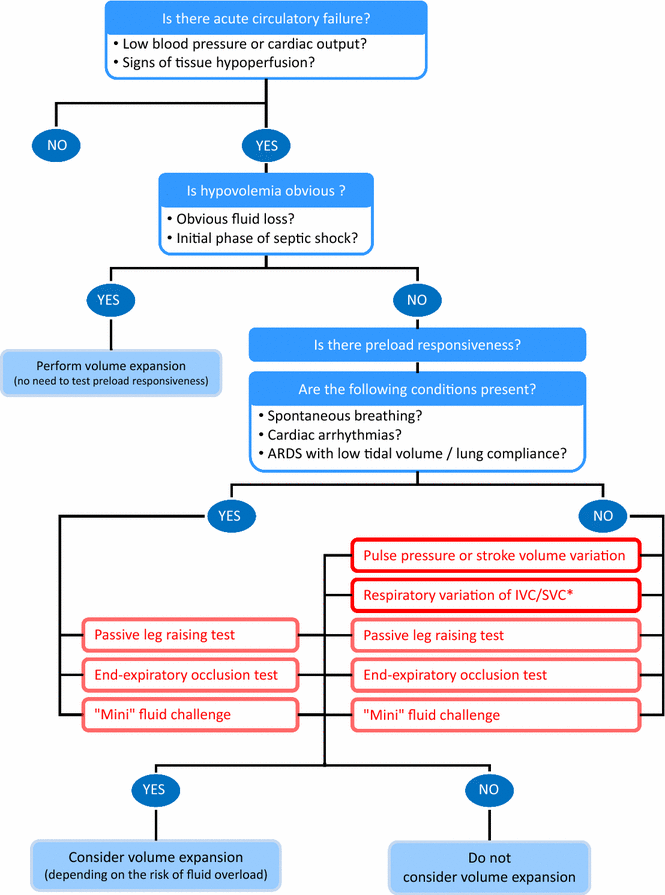
Prediction of fluid responsiveness: an update, Annals of Intensive Care

Dose–response association between fluid overload and in-hospital mortality in critically ill patients: a multicentre, prospective, observational cohort study
Recomendado para você
-
 Overloading and Overriding in C++10 abril 2025
Overloading and Overriding in C++10 abril 2025 -
Can I say”hotness overload “ when talking about someone hot? Or10 abril 2025
-
 Overload Information Shows Overloaded Fact and Answers Stock10 abril 2025
Overload Information Shows Overloaded Fact and Answers Stock10 abril 2025 -
What is Java method overloading? - Quora10 abril 2025
-
 Choice Overload Bias - The Decision Lab10 abril 2025
Choice Overload Bias - The Decision Lab10 abril 2025 -
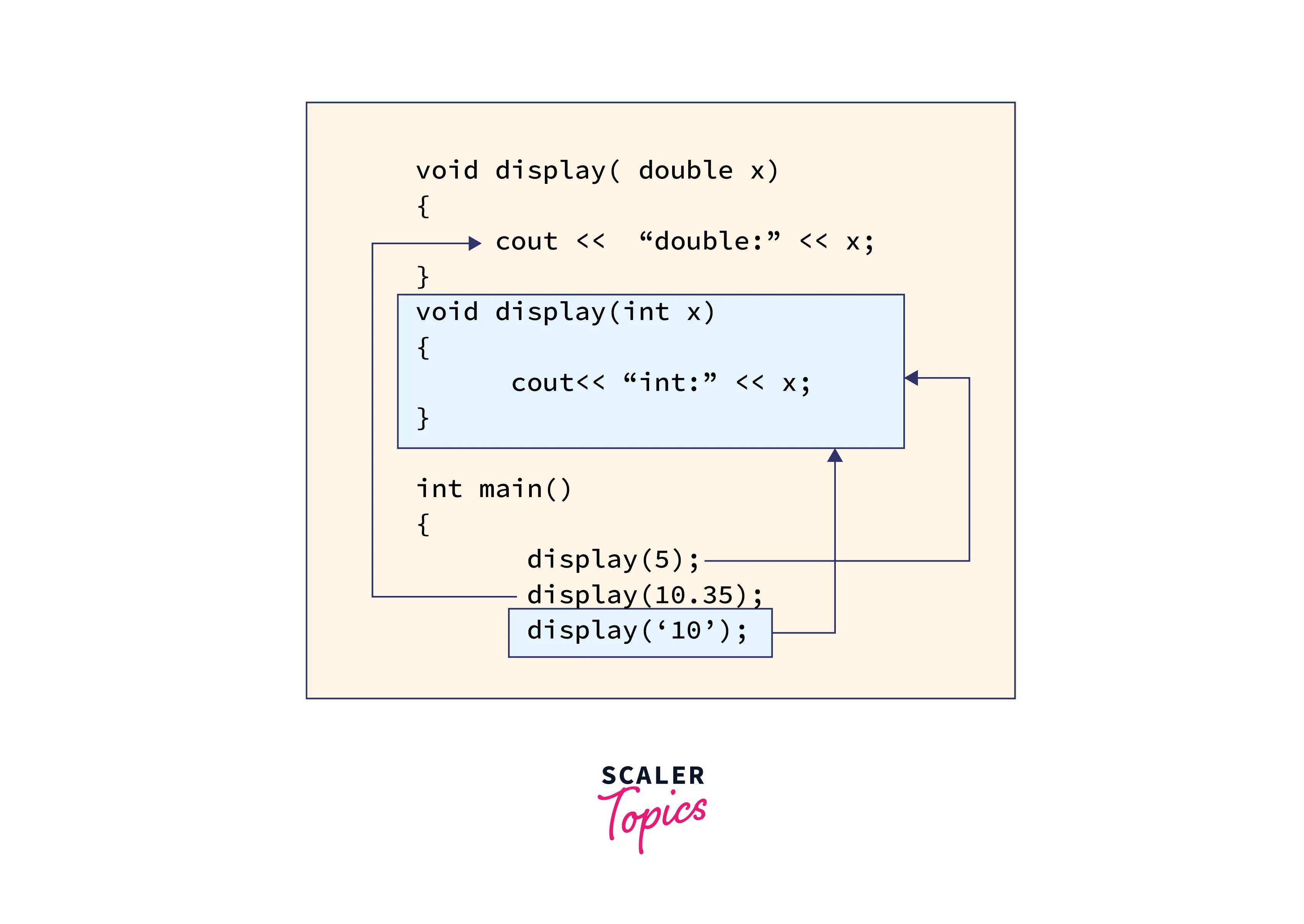 How Can a Call to Overloaded Function Be Ambiguous? - Scaler Topics10 abril 2025
How Can a Call to Overloaded Function Be Ambiguous? - Scaler Topics10 abril 2025 -
 Stressful Word Meaning Pressures Overload And Tension Stock Photo10 abril 2025
Stressful Word Meaning Pressures Overload And Tension Stock Photo10 abril 2025 -
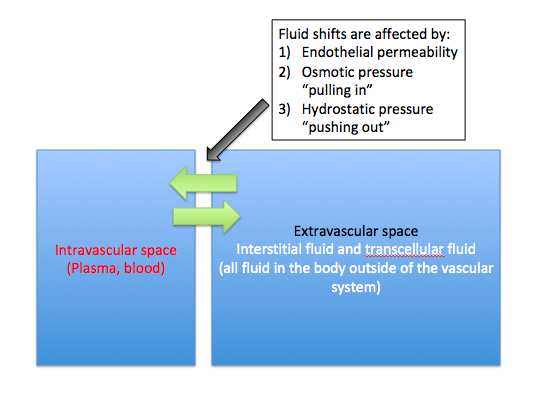 What does it mean to be intravascularly dry but extravascularly10 abril 2025
What does it mean to be intravascularly dry but extravascularly10 abril 2025 -
 What Does 'Cuteness Overload' Mean On TikTok And How Does It10 abril 2025
What Does 'Cuteness Overload' Mean On TikTok And How Does It10 abril 2025 -
 Solved 1. An elevator is designed to tolerate a maximum10 abril 2025
Solved 1. An elevator is designed to tolerate a maximum10 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Fotos de Cabelo bonito, Imagens de Cabelo bonito sem royalties10 abril 2025
Fotos de Cabelo bonito, Imagens de Cabelo bonito sem royalties10 abril 2025 -
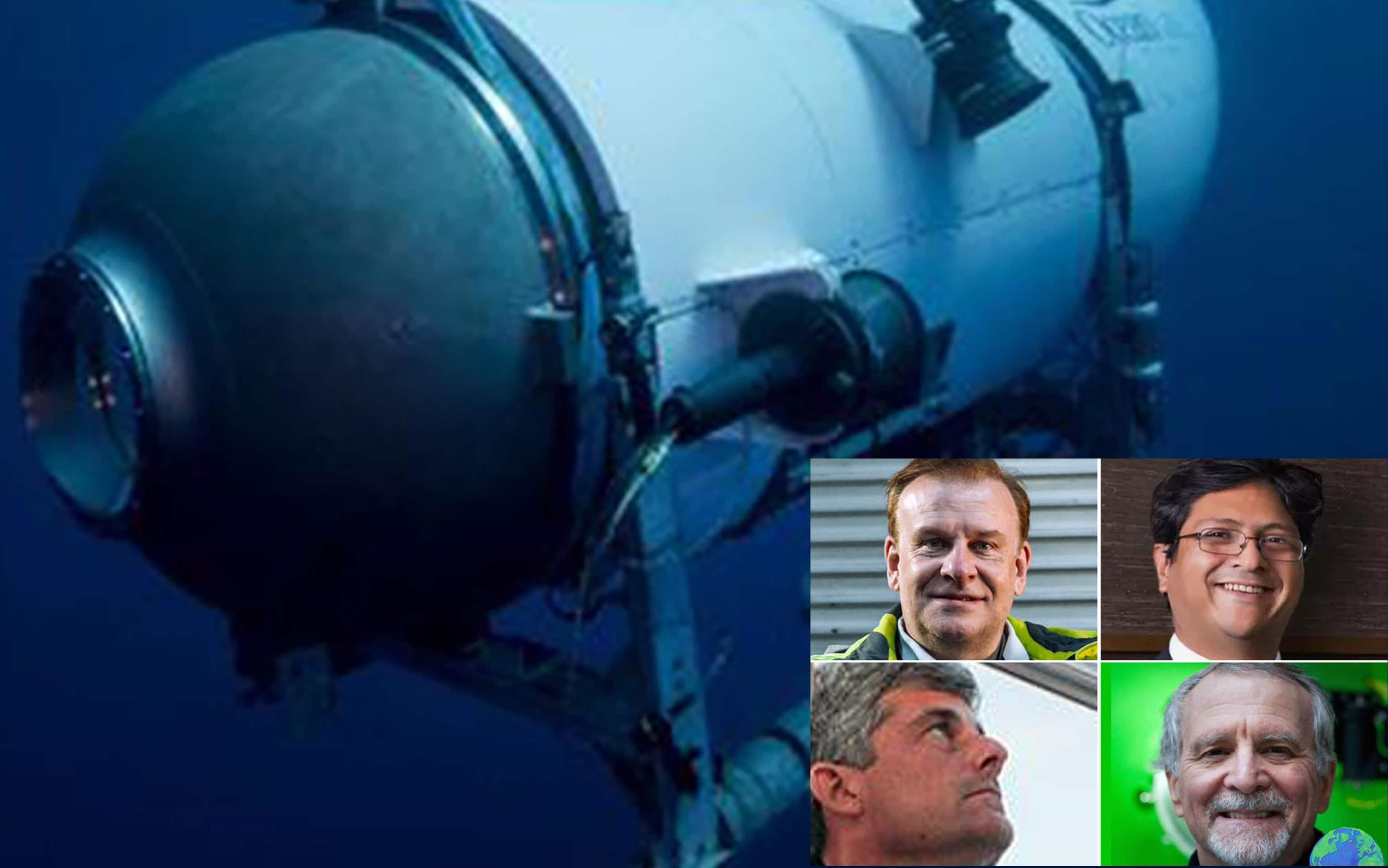 Sottomarino disperso vicino al Titanic, perché le ricerche sono difficili: cosa dicono gli esperti10 abril 2025
Sottomarino disperso vicino al Titanic, perché le ricerche sono difficili: cosa dicono gli esperti10 abril 2025 -
Bispo Jadson Santos added a new photo. - Bispo Jadson Santos10 abril 2025
-
 Beep boop10 abril 2025
Beep boop10 abril 2025 -
 50 Parting Thoughts From the 2023 U.S. Open - Sports Illustrated10 abril 2025
50 Parting Thoughts From the 2023 U.S. Open - Sports Illustrated10 abril 2025 -
 Pin on house ideas10 abril 2025
Pin on house ideas10 abril 2025 -
 Esporte Clube São Carlos completa 71 anos e planeja novidades10 abril 2025
Esporte Clube São Carlos completa 71 anos e planeja novidades10 abril 2025 -
 Tower Defense Simulator Codes 2023 (December) Get Free Gems!10 abril 2025
Tower Defense Simulator Codes 2023 (December) Get Free Gems!10 abril 2025 -
 BAFTA Game Awards 2023: confira a lista de indicados e vote no jogo do ano10 abril 2025
BAFTA Game Awards 2023: confira a lista de indicados e vote no jogo do ano10 abril 2025 -
 Stream Lose My Cool by Moe Vision Listen online for free on SoundCloud10 abril 2025
Stream Lose My Cool by Moe Vision Listen online for free on SoundCloud10 abril 2025
