Performance of Brain-Injured versus Non-Brain-Injured Individuals on Three Versions of the Category Test - Page 120 - UNT Digital Library
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 12 abril 2025
To date, no research exists examining criterion-related validity of alternate, computerized forms of the Category Test. The intent of this study was to address criterion-related validity of three full forms of the Category Test. In that, the goal was to examine equivalency of each version in their ability to differentiate brain-injured from non-brain-injured individuals. Forty-nine (N = 49) healthy adults and 45 (N = 45) brain-injured adults were tested using three versions of the Category Test, the BDI, and the WAIS-R NI. ANOVA indicated no significant differences between versions of the Category Test or an interaction between Category Test version and group membership on the total error score. MANOVA performed between versions of the Category Test and Subtest error scores indicated significant differences between versions on Subtest 3 and Subtest 6. Group membership (brain-injured v. non-brain-injured) produced a significant main effect on all subtests of the Category Test except Subtest 2. Several exploratory analyses were performed examining the relationship between neuropsychological impairment, group membership based on Category Test error scores, and the WAIS-R NI. Clinical applications, such as the use of serial testing to index neurorehabilitation gains, were discussed.

UTRGV School of Medicine, Research Symposium 2019 by UTRGV

The North Texan - UNT Alumni Magazine - Summer 2013 by University

The North Texan - UNT Alumni Magazine - Fall 2018 by University of
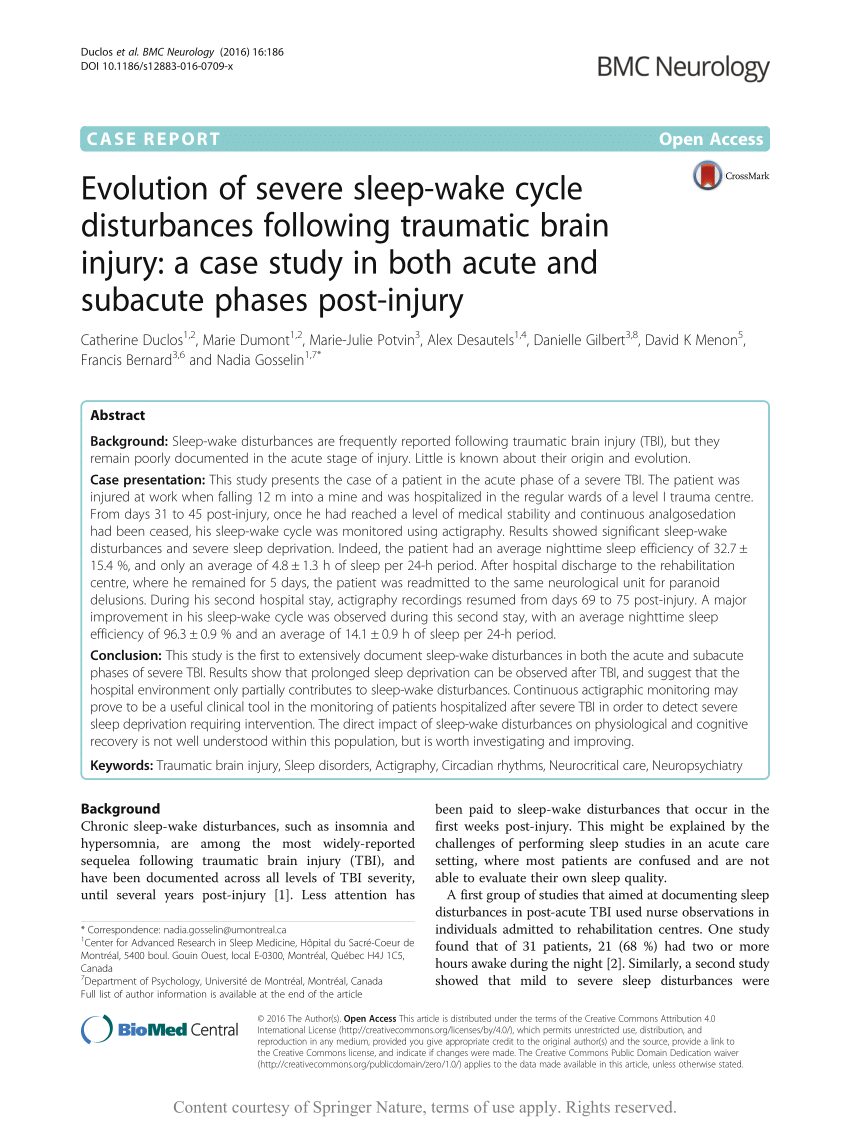
PDF) Evolution of severe sleep-wake cycle disturbances following

Glucuronidated Flavonoids in Neurological Protection: Structural

26th Annual Computational Neuroscience Meeting (CNS*2017): Part 3

PDF) Consensus statement from the international consensus meeting
Early Recognition of Minimal Brain Injury through Use of the

Algorithms and Terrorism: The Malicious Use of Artificial
Performance of Brain-Injured versus Non-Brain-Injured Individuals
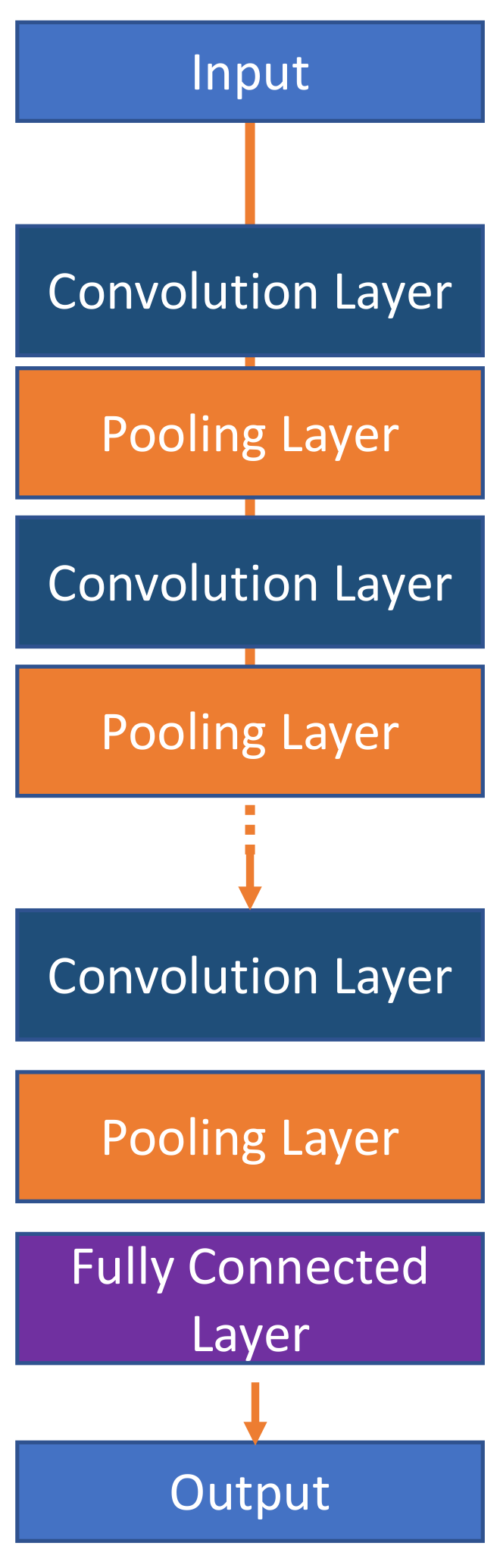
J. Imaging, Free Full-Text
Recomendado para você
-
 Brain Test Level 372 He wants big muscles in 202312 abril 2025
Brain Test Level 372 He wants big muscles in 202312 abril 2025 -
brain test 196|TikTok Search12 abril 2025
-
 Brain Test: Tricky Puzzles Answers for All Levels - Page 37 of 46 - Level Winner12 abril 2025
Brain Test: Tricky Puzzles Answers for All Levels - Page 37 of 46 - Level Winner12 abril 2025 -
UTRGV Office For Sustainability - The Rio Grande Valley - Society For Neuroscience- Chapter (RGV-SFN-C) is organizing several events in its mission of promoting: Outreach, Education, Research in the Neuroscience12 abril 2025
-
 Hereditary multiple exostoses with spinal cord compression.12 abril 2025
Hereditary multiple exostoses with spinal cord compression.12 abril 2025 -
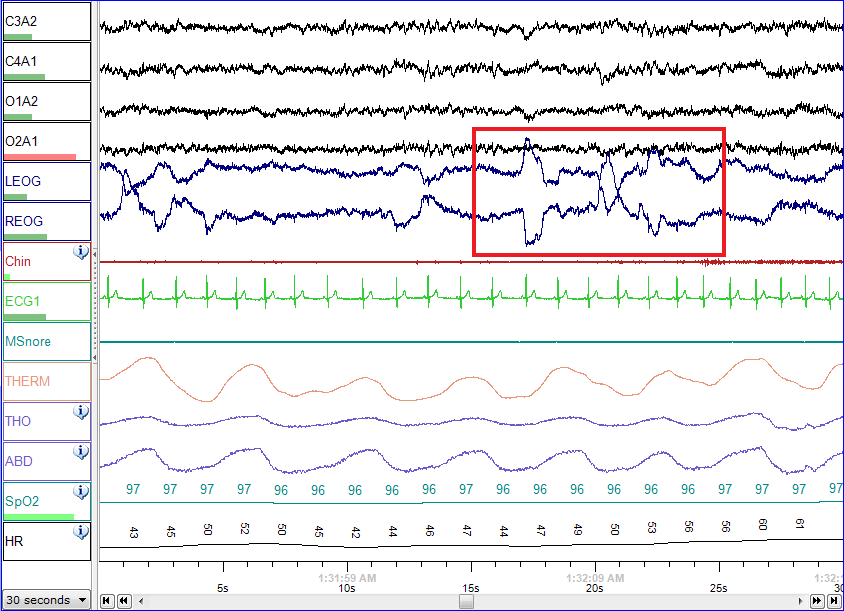 Polysomnography - Wikipedia12 abril 2025
Polysomnography - Wikipedia12 abril 2025 -
 Neuroimaging and deep learning for brain stroke detection - A review of recent advancements and future prospects - ScienceDirect12 abril 2025
Neuroimaging and deep learning for brain stroke detection - A review of recent advancements and future prospects - ScienceDirect12 abril 2025 -
 Different loneliness types, cognitive function, and brain structure in midlife: Findings from the Framingham Heart Study - eClinicalMedicine12 abril 2025
Different loneliness types, cognitive function, and brain structure in midlife: Findings from the Framingham Heart Study - eClinicalMedicine12 abril 2025 -
 Hiding in Plain Sight: Functional Neurological Disorders in the News12 abril 2025
Hiding in Plain Sight: Functional Neurological Disorders in the News12 abril 2025 -
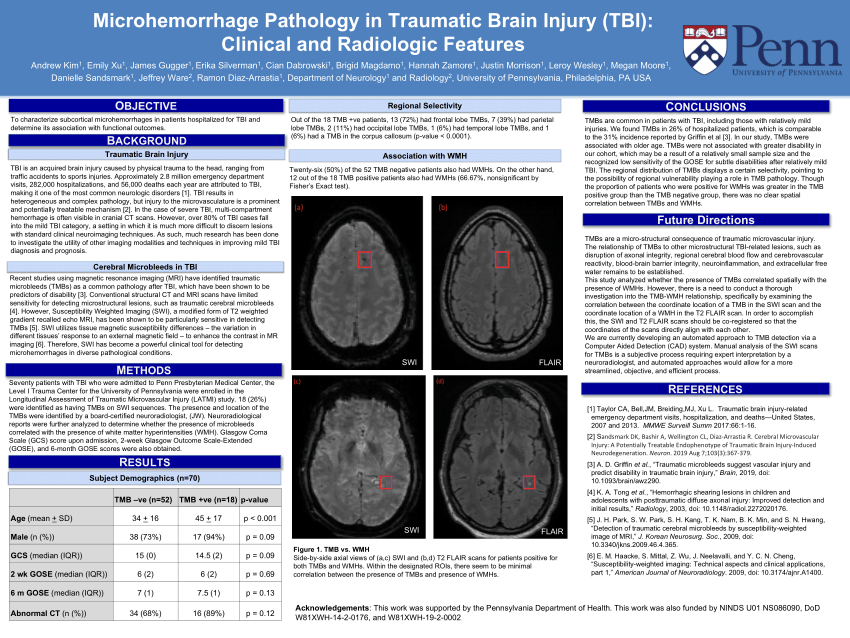 PDF) Microhemorrhage Pathology in Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): Clinical and Radiologic Features12 abril 2025
PDF) Microhemorrhage Pathology in Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): Clinical and Radiologic Features12 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Círculo Cromático: aprenda a combinar cores no look12 abril 2025
Círculo Cromático: aprenda a combinar cores no look12 abril 2025 -
 Brazilian Hot Dog Stock Photo12 abril 2025
Brazilian Hot Dog Stock Photo12 abril 2025 -
 Canadian men's basketball team clinches Olympic berth en route to12 abril 2025
Canadian men's basketball team clinches Olympic berth en route to12 abril 2025 -
 Winners English Training Institute in Marthandam,Kanyakumari - Best Language Classes For English in Kanyakumari - Justdial12 abril 2025
Winners English Training Institute in Marthandam,Kanyakumari - Best Language Classes For English in Kanyakumari - Justdial12 abril 2025 -
 Console Portátil RetroFusion64 em 202312 abril 2025
Console Portátil RetroFusion64 em 202312 abril 2025 -
 Funny cartoon vampire dracula character in 3d holding a movie makers film slate,3d illustration render Stock Photo - Alamy12 abril 2025
Funny cartoon vampire dracula character in 3d holding a movie makers film slate,3d illustration render Stock Photo - Alamy12 abril 2025 -
 Houze Dayz, Interstate12 abril 2025
Houze Dayz, Interstate12 abril 2025 -
 Traje de lapela entalhado xadrez estilo inglês masculino, ternos clássicos masculinos, jaqueta de luxo, calça, colete, colete, slim fit, balzer, 3 peças - AliExpress12 abril 2025
Traje de lapela entalhado xadrez estilo inglês masculino, ternos clássicos masculinos, jaqueta de luxo, calça, colete, colete, slim fit, balzer, 3 peças - AliExpress12 abril 2025 -
 Update – Mirai Nikki Anime! Thoughts Of The Man In The Mind12 abril 2025
Update – Mirai Nikki Anime! Thoughts Of The Man In The Mind12 abril 2025 -
 SLAY Word of the Year: Free Motivational Printables12 abril 2025
SLAY Word of the Year: Free Motivational Printables12 abril 2025

