Assessment of endothelial damage and cardiac injury in a mouse
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 17 abril 2025

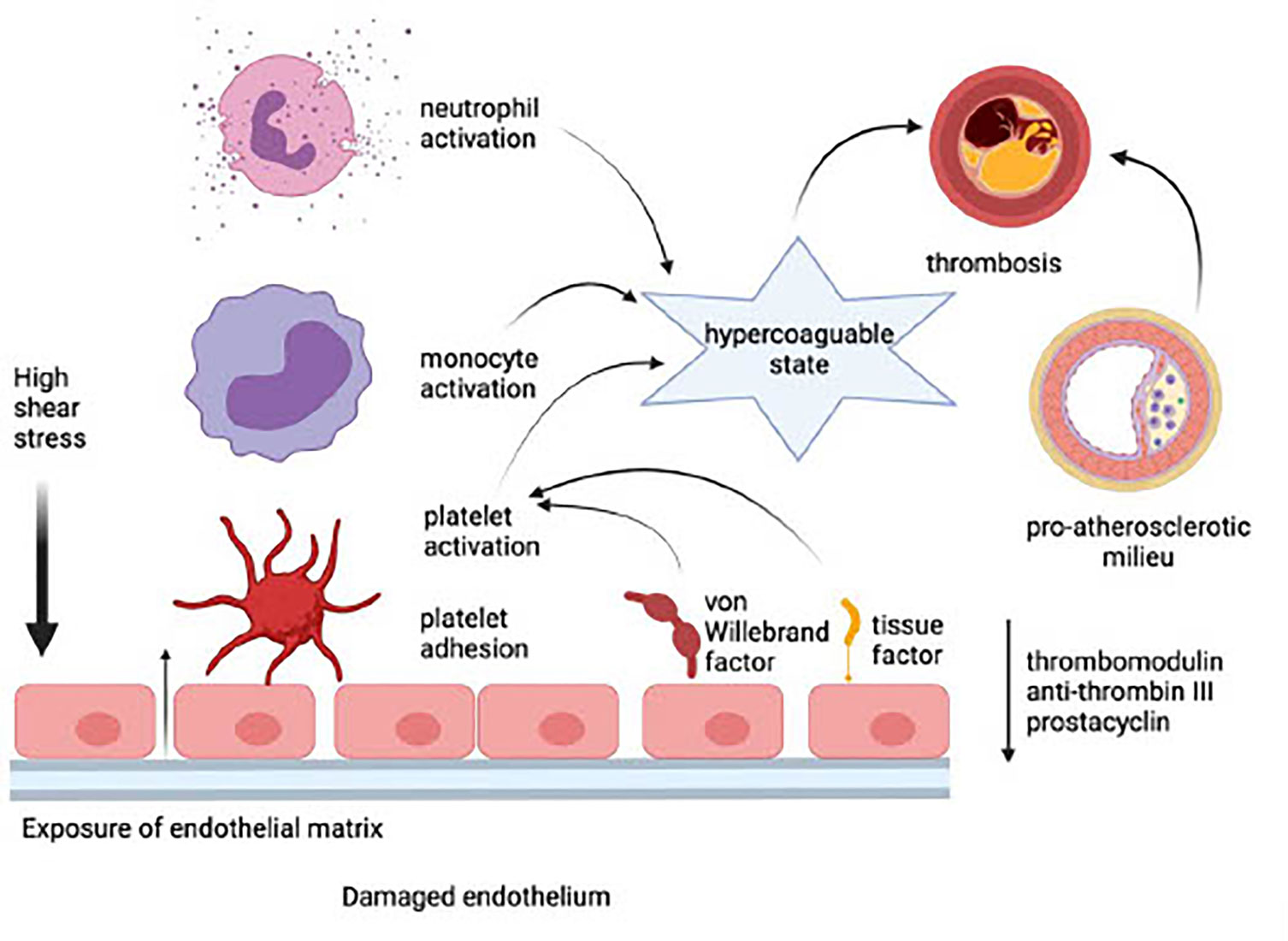
Frontiers Emerging Role of Platelet-Endothelium Interactions in the Pathogenesis of Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection-Associated Myocardial Injury
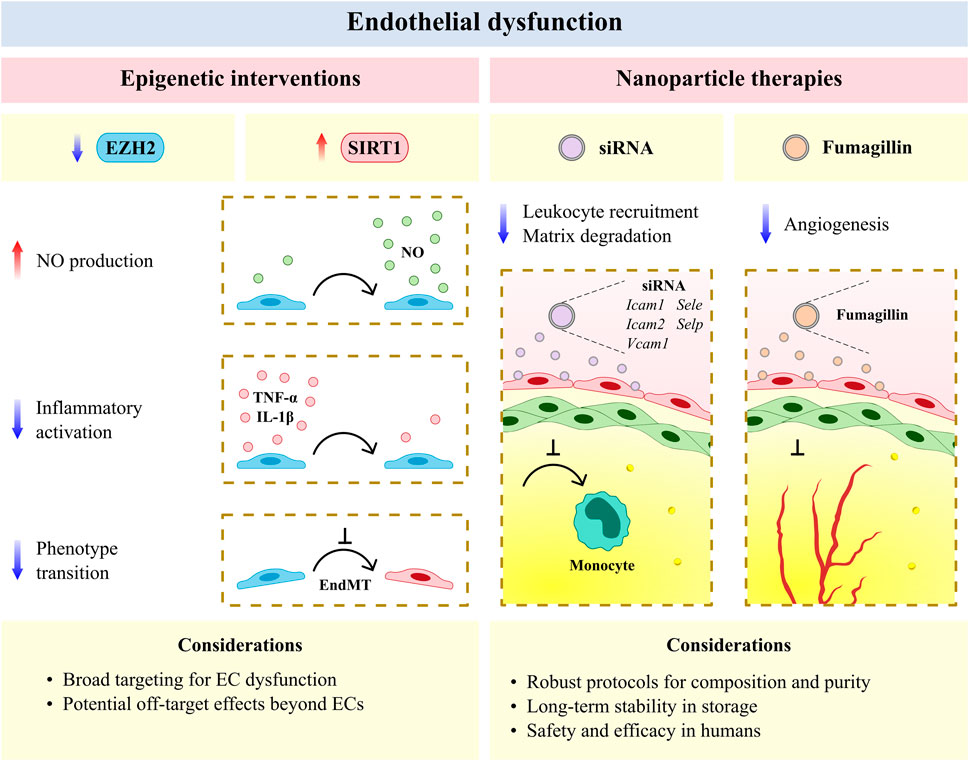
Frontiers Dysfunctional Vascular Endothelium as a Driver of Atherosclerosis: Emerging Insights Into Pathogenesis and Treatment
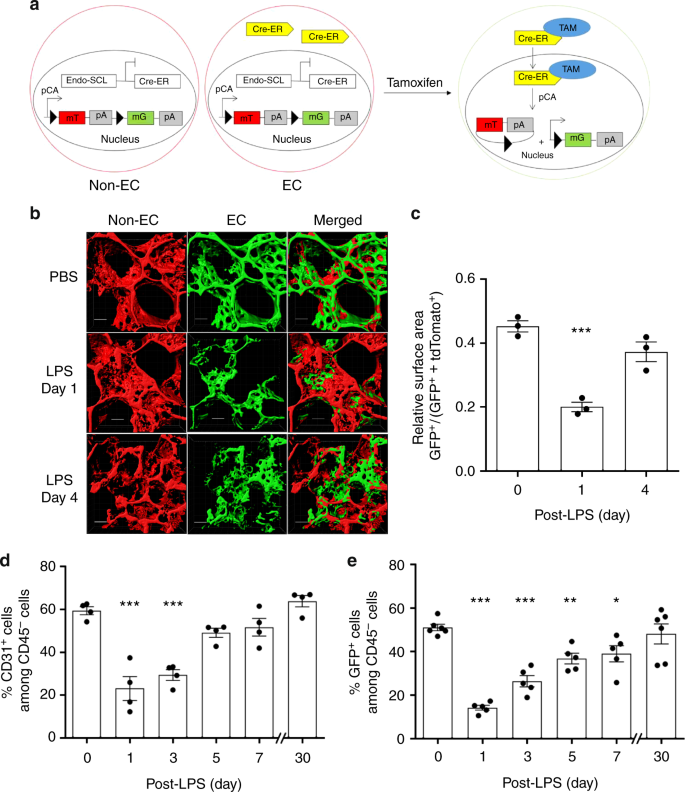
Sox17 is required for endothelial regeneration following inflammation-induced vascular injury

Regeneration and Assessment of the Endothelial Glycocalyx To Address Cardiovascular Disease

Analysis of myocardial cellular gene expression during pressure overload reveals matrix based functional intercellular communication - ScienceDirect

SARS-CoV-2 and the spike protein in endotheliopathy: Trends in Microbiology
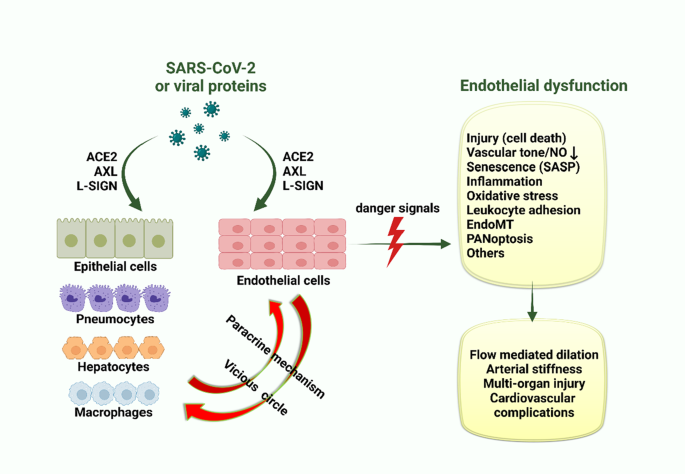
Endothelial dysfunction in COVID-19: an overview of evidence, biomarkers, mechanisms and potential therapies

Biomarkers of endothelial activation and dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases
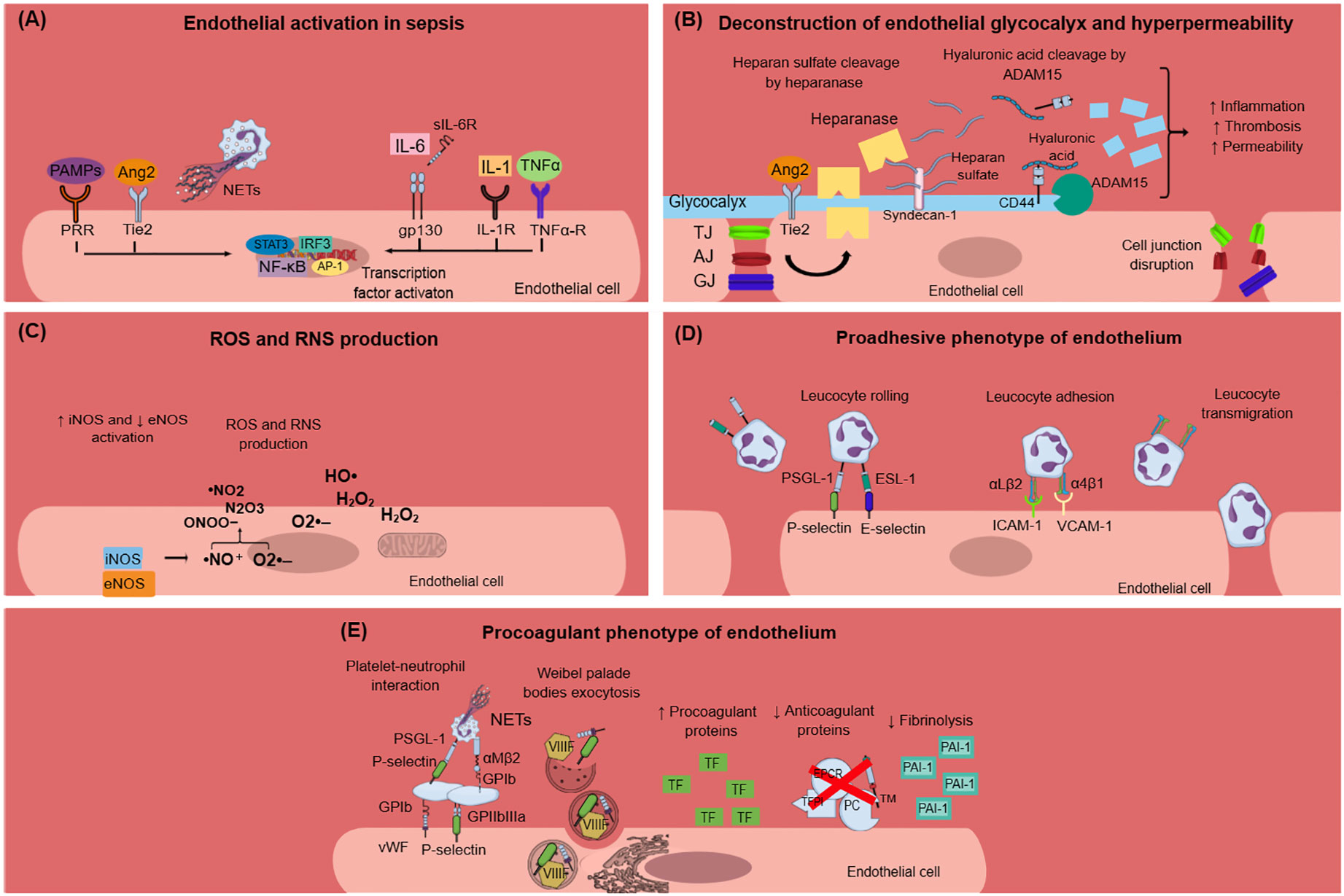
Frontiers Endothelial dysfunction and immunothrombosis in sepsis
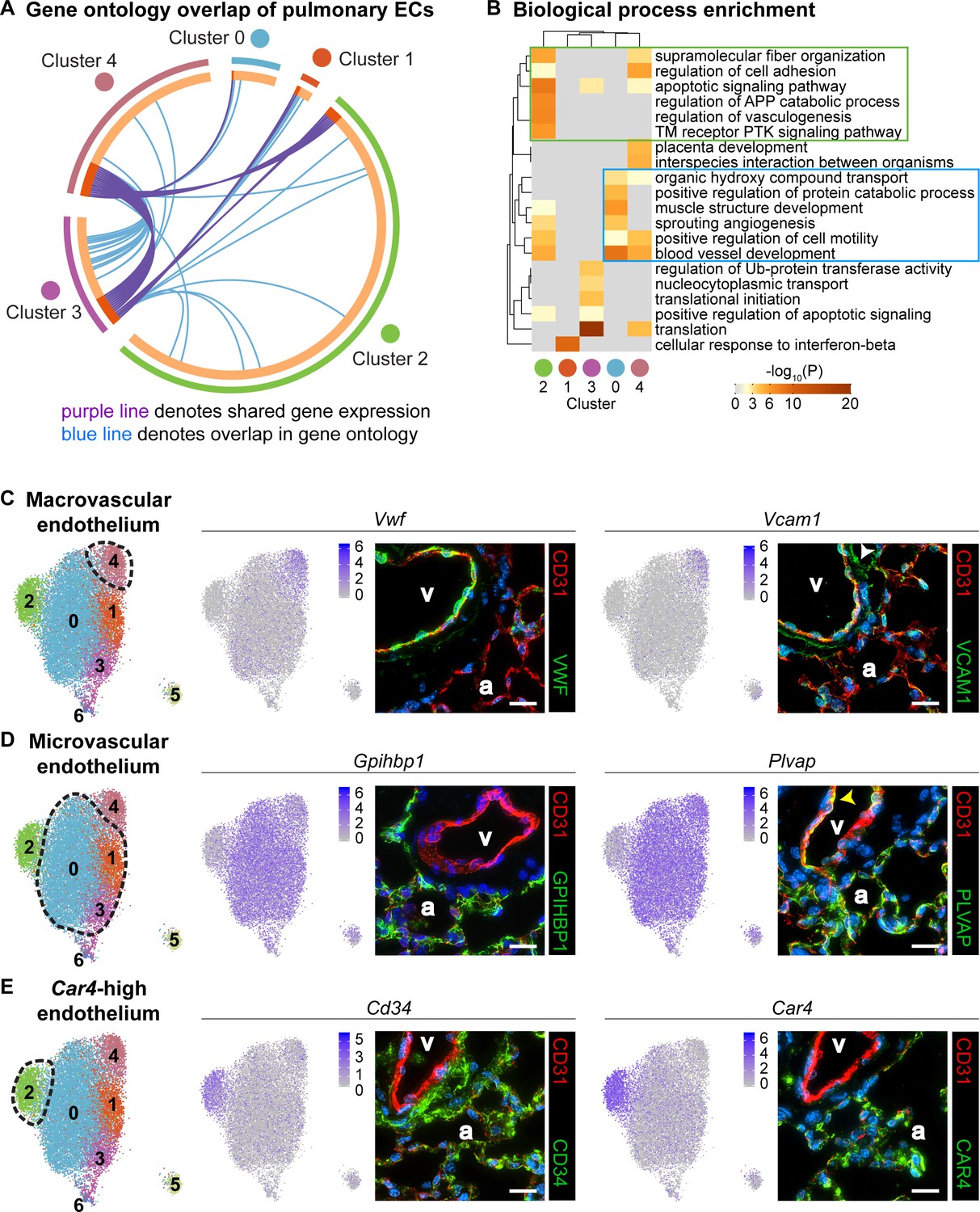
Defining the role of pulmonary endothelial cell heterogeneity in the response to acute lung injury

Endothelial thrombomodulin downregulation caused by hypoxia contributes to severe infiltration and coagulopathy in COVID-19 patient lungs - eBioMedicine

Increased Capillary Permeability in Heart Induces Diastolic Dysfunction Independently of Inflammation, Fibrosis, or Cardiomyocyte Dysfunction
Recomendado para você
-
 Mathilde Boyer Initiative & Finance17 abril 2025
Mathilde Boyer Initiative & Finance17 abril 2025 -
 Vincent DREUX , BNP PARIBAS REAL ESTATE , Business Immo Directory17 abril 2025
Vincent DREUX , BNP PARIBAS REAL ESTATE , Business Immo Directory17 abril 2025 -
 The Earrings of Madame de… – French Institute Alliance Française17 abril 2025
The Earrings of Madame de… – French Institute Alliance Française17 abril 2025 -
 Agathe hi-res stock photography and images - Page 41 - Alamy17 abril 2025
Agathe hi-res stock photography and images - Page 41 - Alamy17 abril 2025 -
 Tim ULINSKI, Head of Pediatric Nephrology Unit17 abril 2025
Tim ULINSKI, Head of Pediatric Nephrology Unit17 abril 2025 -
 for the boys weekend17 abril 2025
for the boys weekend17 abril 2025 -
 Pediatric Pulmonary Hypertension17 abril 2025
Pediatric Pulmonary Hypertension17 abril 2025 -
 Index17 abril 2025
Index17 abril 2025 -
Analysts coverage & consensus17 abril 2025
-
 Valerian and the City of a Thousand Planets/Credits17 abril 2025
Valerian and the City of a Thousand Planets/Credits17 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 NARUTO MODE ERMITE VS SASUKE MANGEKYO SHARINGAN !17 abril 2025
NARUTO MODE ERMITE VS SASUKE MANGEKYO SHARINGAN !17 abril 2025 -
 HOW TO ADD ULTIMATE TROLLING GUI IN YOUR GAMES! (ROBLOX STUDIO17 abril 2025
HOW TO ADD ULTIMATE TROLLING GUI IN YOUR GAMES! (ROBLOX STUDIO17 abril 2025 -
 Decoração SORVETINHO CANDY - A417 abril 2025
Decoração SORVETINHO CANDY - A417 abril 2025 -
 Gamer (2009) - HD Trailer17 abril 2025
Gamer (2009) - HD Trailer17 abril 2025 -
 1000 to 1: The Cory Weissman Story - Wikipedia17 abril 2025
1000 to 1: The Cory Weissman Story - Wikipedia17 abril 2025 -
 Fifa 21: Conheça o aplicativo que permite trocar formações e negociar no FUT - ESPN17 abril 2025
Fifa 21: Conheça o aplicativo que permite trocar formações e negociar no FUT - ESPN17 abril 2025 -
Solved: The Sims 4 Mac Legacy Edition thread - Page 21 - Answer HQ17 abril 2025
-
 Other Grand Piece Online Pika - Game Items - Gameflip17 abril 2025
Other Grand Piece Online Pika - Game Items - Gameflip17 abril 2025 -
 Conjunto de 3 Pôsteres Dinossauros - Miüdo17 abril 2025
Conjunto de 3 Pôsteres Dinossauros - Miüdo17 abril 2025 -
 I love this Gran Turismo feeling with these mods 🫶🏻 : r/assettocorsa17 abril 2025
I love this Gran Turismo feeling with these mods 🫶🏻 : r/assettocorsa17 abril 2025
