Replicatively senescent cells are arrested in G1 and G2 phases - Figure F1
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 12 abril 2025
Senescent human fibroblast cultures contain a large fraction of putative G2-arrested cells with 4N DNA content. (A) Propidium iodide (PI) staining and flow cyctometric analysis of HCA2 normal human foreskin fibroblasts. Cells entered senescence at PD73. (B) PI staining of replicatively senescent human lung fibroblasts WI-38, and IMR-90 at PDs 73 and 68 respectively. (C) The fraction of 4N cells in senescent cell population does not diminish with time. Replicatively senescent HCA2 cells were analyzed by PI staining at weekly intervals for 10 weeks stating from the onset of senescence.

Senescent BT-20 cells with PRL-3 knockdown arrest in G1 despite

Figure 3 from SUN1 silencing inhibits cell growth through G0/G1

Cellular senescence preserves viral genome maintenance

PDF) Possibility of inducing tumor cell senescence during therapy

Exploiting replicative stress in gynecological cancers as a
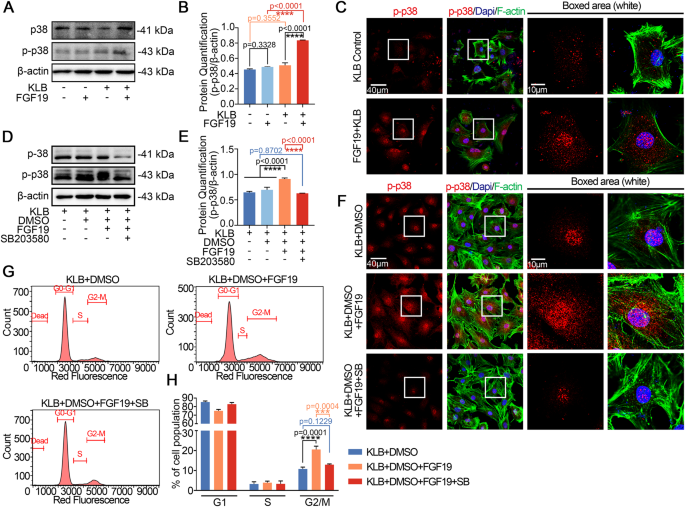
FGF19 induces the cell cycle arrest at G2-phase in chondrocytes

Telomeric dysfunction triggers an unstable growth arrest leading

Cell cycle re-entry and arrest in G2/M phase induces senescence
TGF-β induces corneal endothelial senescence via increase of
Deferoxamine accelerates endothelial progenitor cell senescence

Expansion and Cell-Cycle Arrest: Common Denominators of Cellular
T cell senescence and p21 in systemic autoimmunity. In lupus-prone

Cell cycle analysis of senescent astrocytes. (A) Representative
Recomendado para você
-
 Pay no attention to the Formula 1 race car, he's a spy. G1 Mirage!12 abril 2025
Pay no attention to the Formula 1 race car, he's a spy. G1 Mirage!12 abril 2025 -
 Power HD Aluminum G1 High Stability Gyro Red For RC Car Drift F1 Touring On Road12 abril 2025
Power HD Aluminum G1 High Stability Gyro Red For RC Car Drift F1 Touring On Road12 abril 2025 -
 Pre-Owned Vizio OEM Remote Control for VIZIO Smart TV D50x-G9 D65x-G4 D55x-G1 D40f-G9 D43f-F1 D70-F3 V505-G9 D32h-F1 D24h-G9 E70-F3 D43-F1 V705-G312 abril 2025
Pre-Owned Vizio OEM Remote Control for VIZIO Smart TV D50x-G9 D65x-G4 D55x-G1 D40f-G9 D43f-F1 D70-F3 V505-G9 D32h-F1 D24h-G9 E70-F3 D43-F1 V705-G312 abril 2025 -
 KAWASAKI GA2-90SS-G1-M11-J1-J1T-D1-B1-F1-F2 EMBLEM FUEL TANK REPRO RASIN12 abril 2025
KAWASAKI GA2-90SS-G1-M11-J1-J1T-D1-B1-F1-F2 EMBLEM FUEL TANK REPRO RASIN12 abril 2025 -
 IIVVERR 20mm F1/2 G1/2 Thread 1.5M Long Shower Hose Pipe for Hand Held Showerhead (20mm F1 / 2' 'G1 / 2' 'Tubo de manguera de ducha larga de 1.5M12 abril 2025
IIVVERR 20mm F1/2 G1/2 Thread 1.5M Long Shower Hose Pipe for Hand Held Showerhead (20mm F1 / 2' 'G1 / 2' 'Tubo de manguera de ducha larga de 1.5M12 abril 2025 -
G1 (@G1Official) / X12 abril 2025
-
 Filtrete™ Room Air Purifier - Small Room – FAP-C01BA-G1, 110 Sq Ft12 abril 2025
Filtrete™ Room Air Purifier - Small Room – FAP-C01BA-G1, 110 Sq Ft12 abril 2025 -
 Check Out This Aprilia RSV4-Powered Race Car - Asphalt & Rubber12 abril 2025
Check Out This Aprilia RSV4-Powered Race Car - Asphalt & Rubber12 abril 2025 -
 EBC Kawasaki ZX-6R (ZX 600 F1/F2/F3/G1/G2) 95-99 SRC Race/Sport Kevlar Series Clutch Kit - Sportbike Track Gear12 abril 2025
EBC Kawasaki ZX-6R (ZX 600 F1/F2/F3/G1/G2) 95-99 SRC Race/Sport Kevlar Series Clutch Kit - Sportbike Track Gear12 abril 2025 -
 LEGO MOC Transformers G1 Mirage Mini Mecha by FreshBricks12 abril 2025
LEGO MOC Transformers G1 Mirage Mini Mecha by FreshBricks12 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 How to Fix Error You Must Perform a System Update to play Zelda BoTW in Cemu Emulator12 abril 2025
How to Fix Error You Must Perform a System Update to play Zelda BoTW in Cemu Emulator12 abril 2025 -
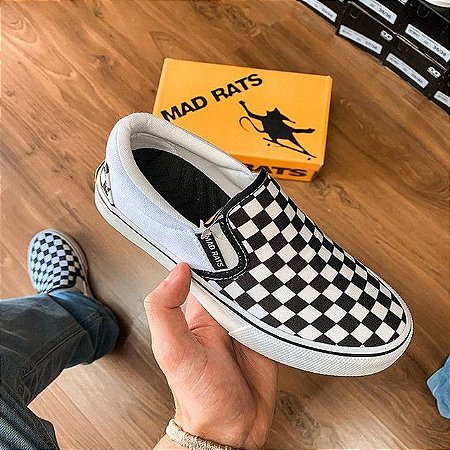 Tênis Slip On Xadrez Mad Rats Unissex - Maduda Shop12 abril 2025
Tênis Slip On Xadrez Mad Rats Unissex - Maduda Shop12 abril 2025 -
 Fnaf 1 Animatronics 3D - TurboSquid 210178312 abril 2025
Fnaf 1 Animatronics 3D - TurboSquid 210178312 abril 2025 -
 Elden Ring Benchmark Test & Performance Analysis Review - Performance & VRAM Usage12 abril 2025
Elden Ring Benchmark Test & Performance Analysis Review - Performance & VRAM Usage12 abril 2025 -
 Level -0 - Untextured The Backrooms Experience: Alternative12 abril 2025
Level -0 - Untextured The Backrooms Experience: Alternative12 abril 2025 -
Pokémon World Center - ALOLA!!! Fiquei um bom tempo foraCerca de um ano hehehe mas vamos tentar voltar com a páginaVamos voltando com um Top 5 melhores pokemons de alola? 5° Lugar12 abril 2025
-
 O SIGNIFICADO DAS CORES EM DRAGON BALL12 abril 2025
O SIGNIFICADO DAS CORES EM DRAGON BALL12 abril 2025 -
 TBH is short for The Binding hOfIsaac12 abril 2025
TBH is short for The Binding hOfIsaac12 abril 2025 -
 fnf vs mickzwmusz pibby 11282013 - Illustrations ART street12 abril 2025
fnf vs mickzwmusz pibby 11282013 - Illustrations ART street12 abril 2025 -
 Funny Pop Music Cat Dancing Sticker for Sale by THANKS4BUYING12 abril 2025
Funny Pop Music Cat Dancing Sticker for Sale by THANKS4BUYING12 abril 2025

