Hydrology, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 19 outubro 2024
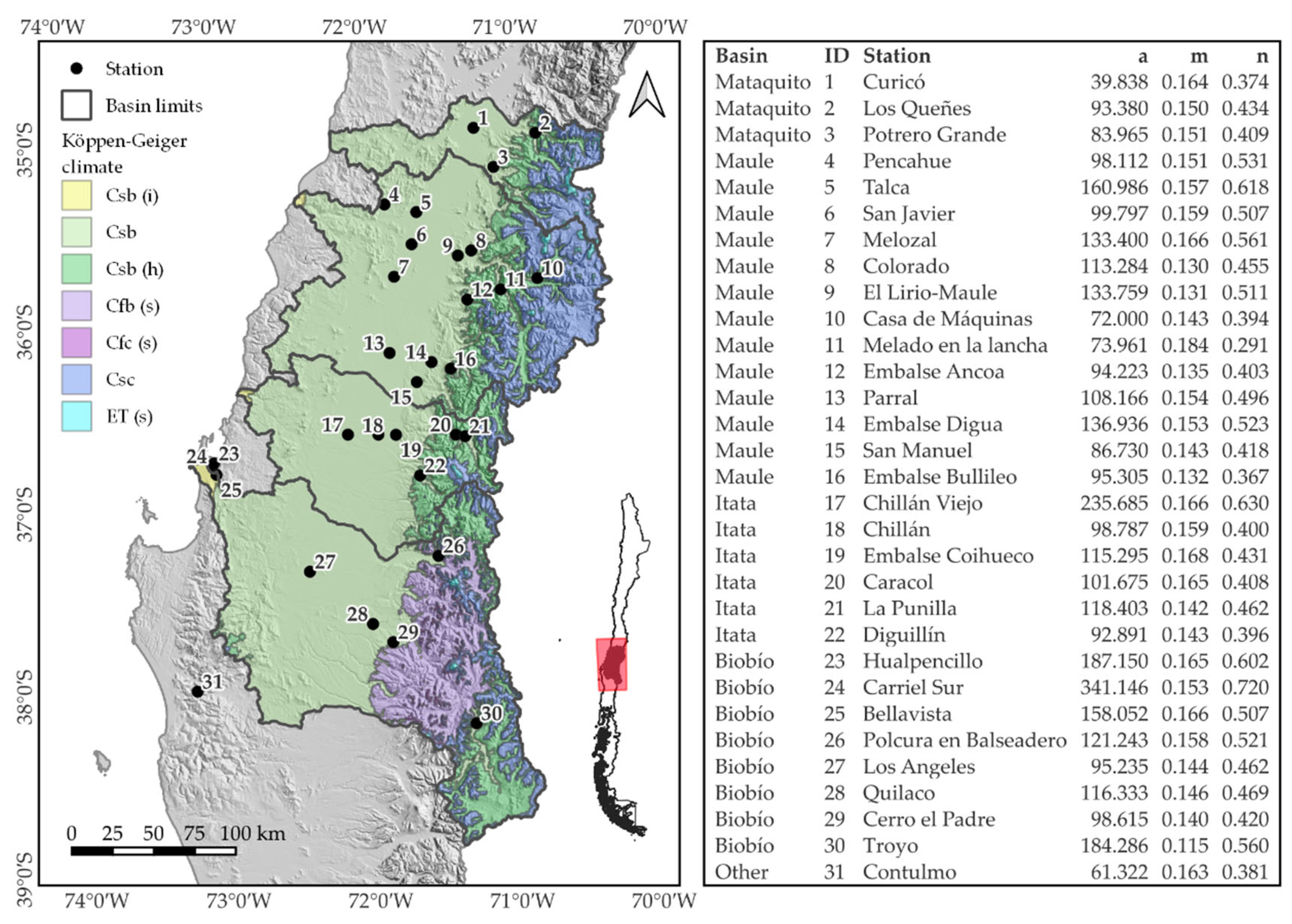
Estimating intensity−duration−frequency (IDF) curves requires local historical information of precipitation intensity. When such information is unavailable, as in areas without rain gauges, it is necessary to consider other methods to estimate curve parameters. In this study, three methods were explored to estimate IDF curves in ungauged areas: Kriging (KG), Inverse Distance Weighting (IDW), and Storm Index (SI). To test the viability of these methods, historical data collected from 31 rain gauges distributed in central Chile, 35° S to 38° S, are used. As a result of the reduced number of rain gauges to evaluate the performance of each method, we used LOOCV (Leaving One Out Cross Validation). The results indicate that KG was limited due to the sparse distribution of rain gauges in central Chile. SI (a linear scaling method) showed the smallest prediction error in all of the ungauged locations, and outperformed both KG and IDW. However, the SI method does not provide estimates of uncertainty, as is possible with KG. The simplicity of SI renders it a viable method for extrapolating IDF curves to locations without data in the central zone of Chile.

Hydrological Processes, Hydrology Journal
B R Chahar Ground Water Hydrology Download Pdf - Colaboratory

Geosciences, Free Full-Text
HESS - Home
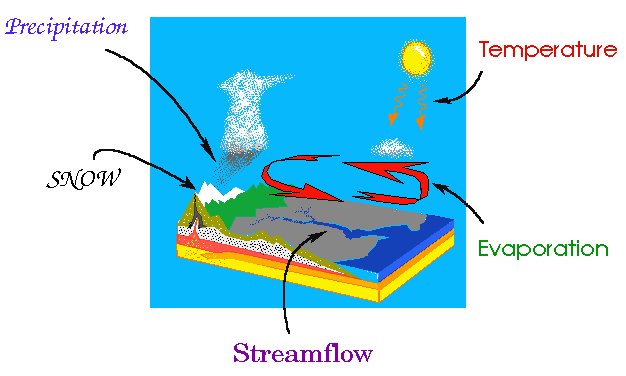
Description of Hydrologic Cycle

Journal of Hydrology by Elsevier
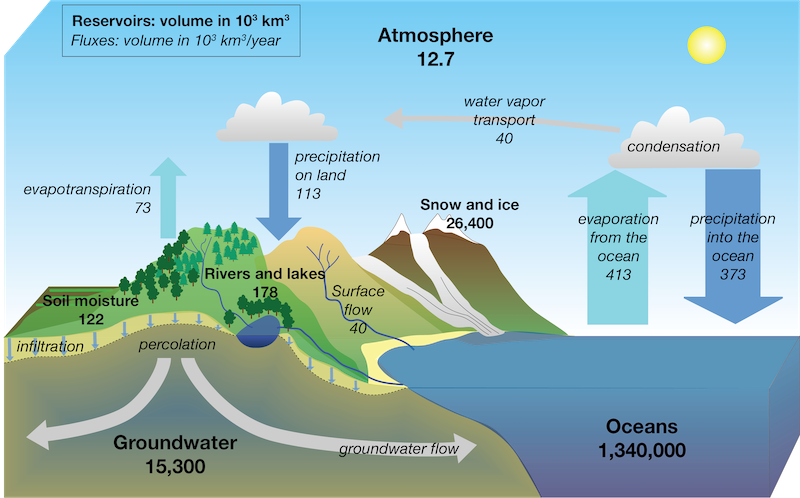
The Hydrologic Cycle, Earth Science

Basic Hydrology

Fitting the Curve: Flood Frequency Analyses – Surface Water

Hydrology for engineers : Linsley, Ray K : Free Download, Borrow
6 Global Hydrological Cycles and Water Resources
Recomendado para você
-
 Se anuncian los nominados a The Game Awards 202219 outubro 2024
Se anuncian los nominados a The Game Awards 202219 outubro 2024 -
 News program hi-res stock photography and images - Alamy19 outubro 2024
News program hi-res stock photography and images - Alamy19 outubro 2024 -
 Horario estelar (2023) - Filmaffinity19 outubro 2024
Horario estelar (2023) - Filmaffinity19 outubro 2024 -
 La hora marcada (2023) - Filmaffinity19 outubro 2024
La hora marcada (2023) - Filmaffinity19 outubro 2024 -
Valpo Surf Project19 outubro 2024
-
 UEFA 2022-23 Champions League group stage draw: how to watch on TV19 outubro 2024
UEFA 2022-23 Champions League group stage draw: how to watch on TV19 outubro 2024 -
 Vivencias Travel - All You Need to Know BEFORE You Go (with Photos)19 outubro 2024
Vivencias Travel - All You Need to Know BEFORE You Go (with Photos)19 outubro 2024 -
Andrew B. Raupp - Founder & CEO - STEM.org19 outubro 2024
-
 Street lamps can increase thyroid cancer risk by 55%19 outubro 2024
Street lamps can increase thyroid cancer risk by 55%19 outubro 2024 -
 Tribeca Festival Announces 2023 Short Film Lineup - Nerds and Beyond19 outubro 2024
Tribeca Festival Announces 2023 Short Film Lineup - Nerds and Beyond19 outubro 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Dragon Ball Super Super Hero TIMELINE PLACEMENT! Is It BEFORE or AFTER Moro & Granolah?19 outubro 2024
Dragon Ball Super Super Hero TIMELINE PLACEMENT! Is It BEFORE or AFTER Moro & Granolah?19 outubro 2024 -
 Internet Memes And 'The Right To Be Forgotten' : All Tech Considered : NPR19 outubro 2024
Internet Memes And 'The Right To Be Forgotten' : All Tech Considered : NPR19 outubro 2024 -
 What If Naruto & Sasuke Travel back in time During Second Shinobi War Part 319 outubro 2024
What If Naruto & Sasuke Travel back in time During Second Shinobi War Part 319 outubro 2024 -
 Na China, streamer é uma profissão em ascensão - Ibrachina19 outubro 2024
Na China, streamer é uma profissão em ascensão - Ibrachina19 outubro 2024 -
 CapCut_duda rubert dançando botada bruta19 outubro 2024
CapCut_duda rubert dançando botada bruta19 outubro 2024 -
 best stats for gs auto clicker|TikTok Search19 outubro 2024
best stats for gs auto clicker|TikTok Search19 outubro 2024 -
 Rebel Moon – Parte 1: A Menina do Fogo: Veja sinopse, elenco e trailer do filme de Zack Snyder19 outubro 2024
Rebel Moon – Parte 1: A Menina do Fogo: Veja sinopse, elenco e trailer do filme de Zack Snyder19 outubro 2024 -
 Mamahaha no Tsurego ga Moto Kano Datta - 1º Trailer do anime19 outubro 2024
Mamahaha no Tsurego ga Moto Kano Datta - 1º Trailer do anime19 outubro 2024 -
 Codigos de camisas de time e seleção no brookhaven #shorts #brookhaven #roblox em 202319 outubro 2024
Codigos de camisas de time e seleção no brookhaven #shorts #brookhaven #roblox em 202319 outubro 2024 -
 how to play roblox on school chrome book|TikTok Search19 outubro 2024
how to play roblox on school chrome book|TikTok Search19 outubro 2024

