Cureus, Whole-Exome Sequencing Identified a Novel DYRK1A Variant in a Patient With Intellectual Developmental Disorder, Autosomal Dominant 7
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 12 abril 2025
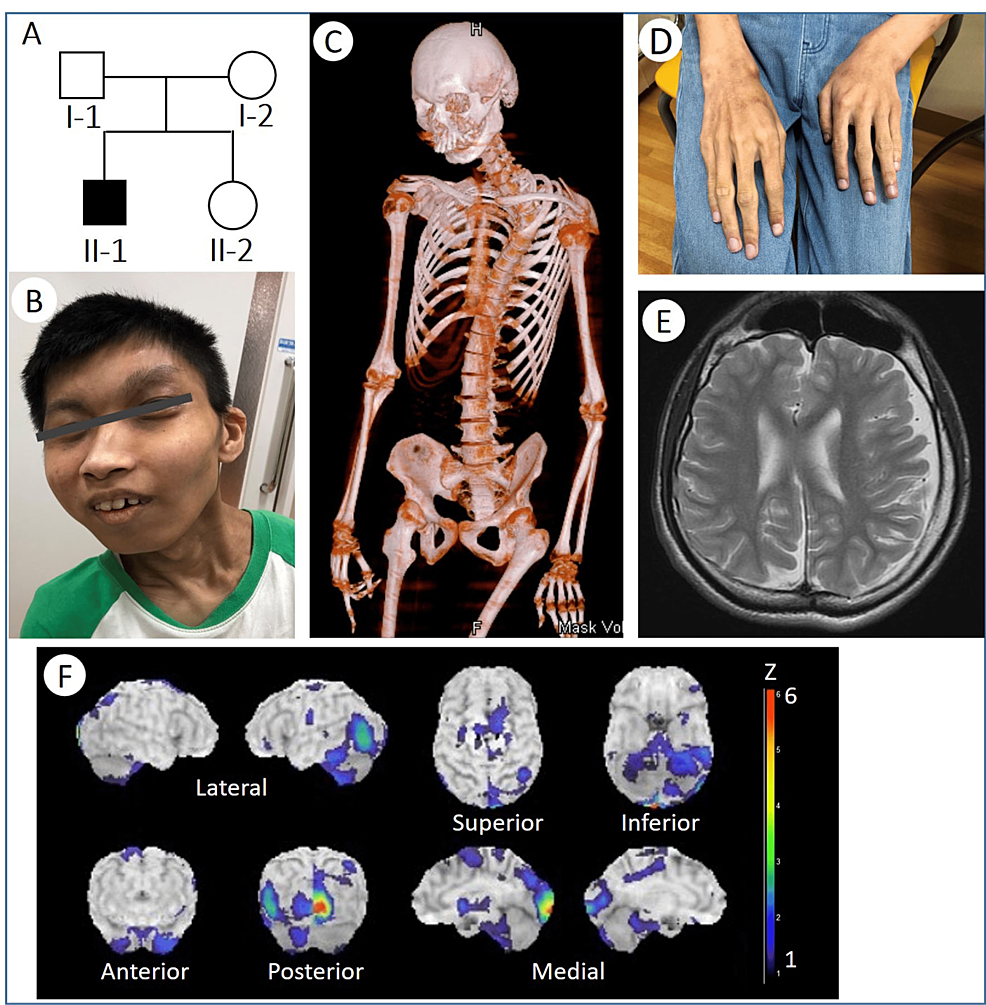
Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal dominant 7 (MRD7; OMIM 614104) is a rare disease characterized by microcephaly, intellectual disability, speech delay, feeding difficulties, and facial dysmorphisms. This disorder is caused by pathogenic/likely pathogenic variants of the DYRK1A gene, which encodes dual-specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A. Here, we report a case of MRD7 that was diagnosed using Face2Gene and whole-exome sequencing (WES). A 22-year-old man presented with microcephaly, intellectual disability, slender body, long slender fingers, and facial dysmorphisms. He was previously diagnosed with Cornelia de Lange syndrome (CdLS) at four years of age. However, his CdLS clinical diagnostic score was low at 22 years of age. The Face2Gene application introduced several candidate diseases including MRD7. Finally, by utilizing WES and Sanger sequencing analysis of cloned cDNA, we identified a novel heterozygous duplication variant (c.848dup, p.(Asn283LysfsTer6)) in the DYRK1A gene, which introduces a premature stop codon. This report provides more information about the phenotypic spectrum of a young adult patient with MRD7. Face2Gene helped us introduce candidate diseases of the patient. Registering further genetically confirmed cases with MRD7 will improve the accuracy of the diagnostic recommendations in Face2Gene. Moreover, WES is a powerful tool for diagnosing rare genetic diseases, such as MRD7.
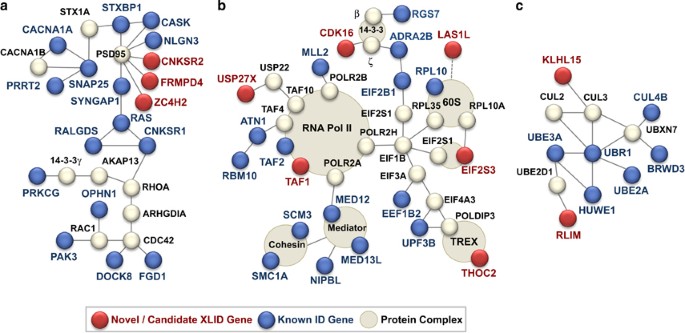
X-exome sequencing of 405 unresolved families identifies seven novel intellectual disability genes

De Novo Disruption of the Proteasome Regulatory Subunit PSMD12 Causes a Syndromic Neurodevelopmental Disorder. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Whole exome and targeted gene sequencing to detect pathogenic recessive variants in early onset cerebellar ataxia - Shakya - 2019 - Clinical Genetics - Wiley Online Library
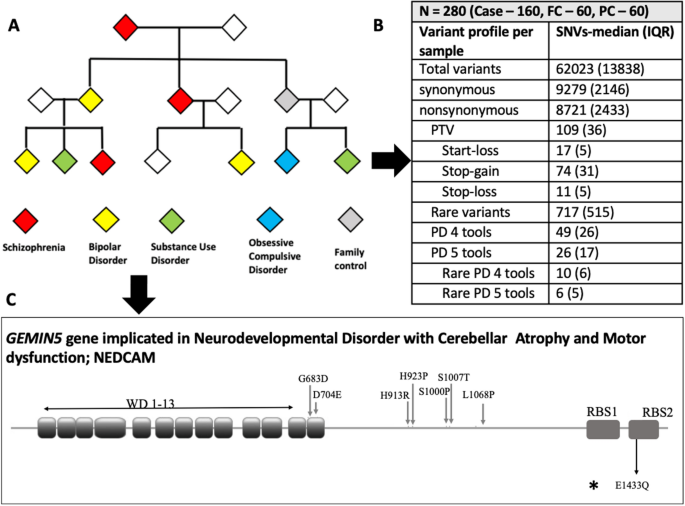
Whole exome sequencing in dense families suggests genetic pleiotropy amongst Mendelian and complex neuropsychiatric syndromes

Cureus, Whole-Exome Sequencing Identified a Novel DYRK1A Variant in a Patient With Intellectual Developmental Disorder, Autosomal Dominant 7
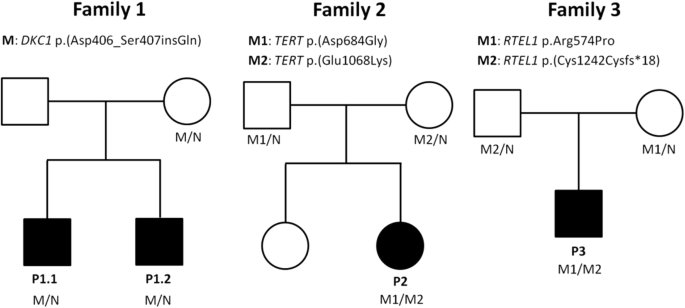
Diagnostics of rare disorders: whole-exome sequencing deciphering locus heterogeneity in telomere biology disorders, Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases

Clinical Whole-Exome Sequencing for the Diagnosis of Mendelian Disorders
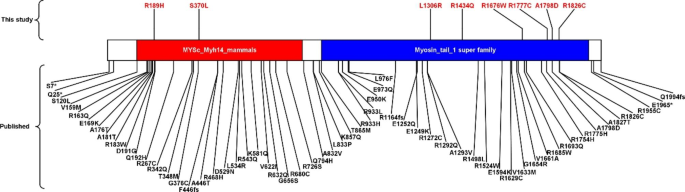
Whole-exome sequencing analysis identifies novel variants associated with Kawasaki disease susceptibility, Pediatric Rheumatology

PDF) Next Generation Sequencing in Autism Spectrum Disorder
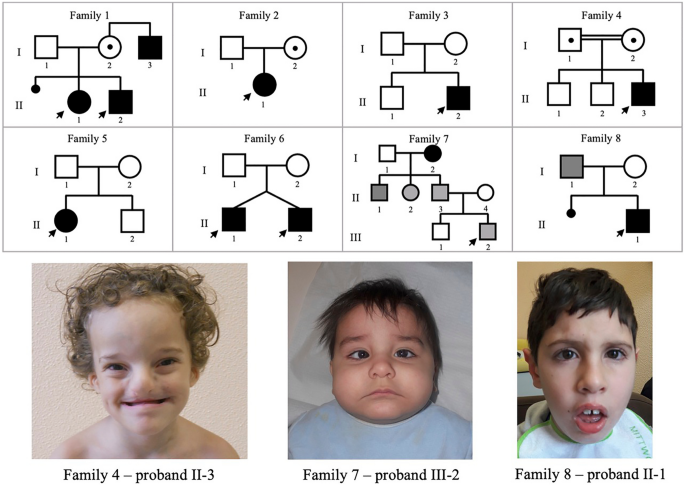
Pitfalls of whole exome sequencing in undefined clinical conditions with a suspected genetic etiology
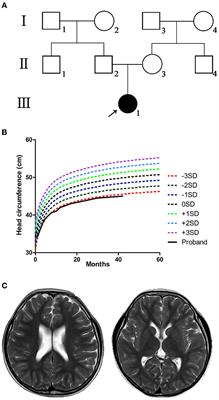
Frontiers Case report: A novel de novo deletion mutation of DYRK1A is associated with intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal dominant 7
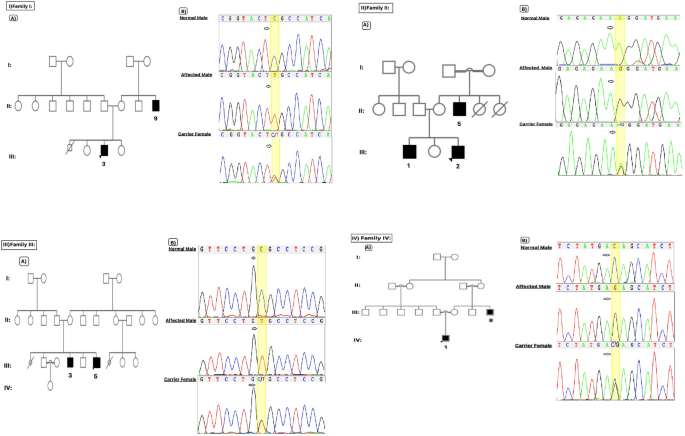
Whole exome sequencing revealed variants in four genes underlying X-linked intellectual disability in four Iranian families: novel deleterious variants and clinical features with the review of literature, BMC Medical Genomics
Publications using Face2Gene - Face2Gene
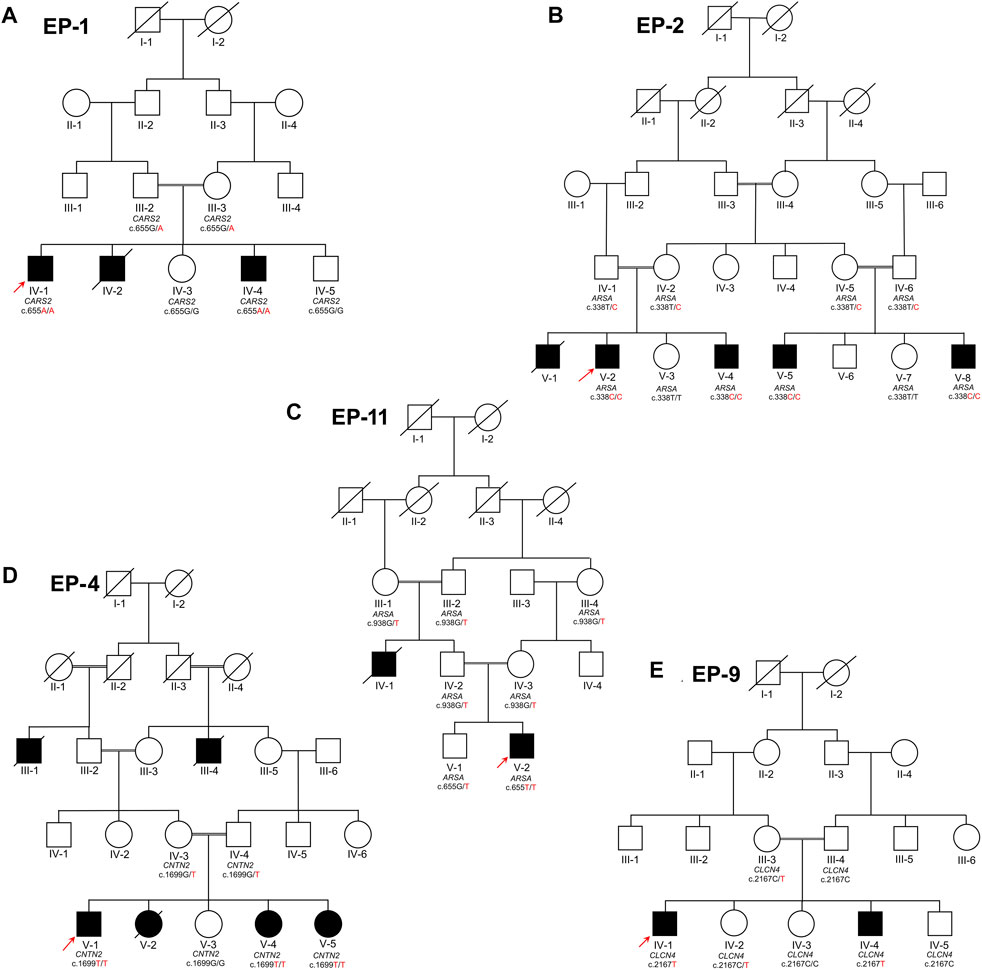
Frontiers Whole exome sequencing identified five novel variants in CNTN2, CARS2, ARSA, and CLCN4 leading to epilepsy in consanguineous families
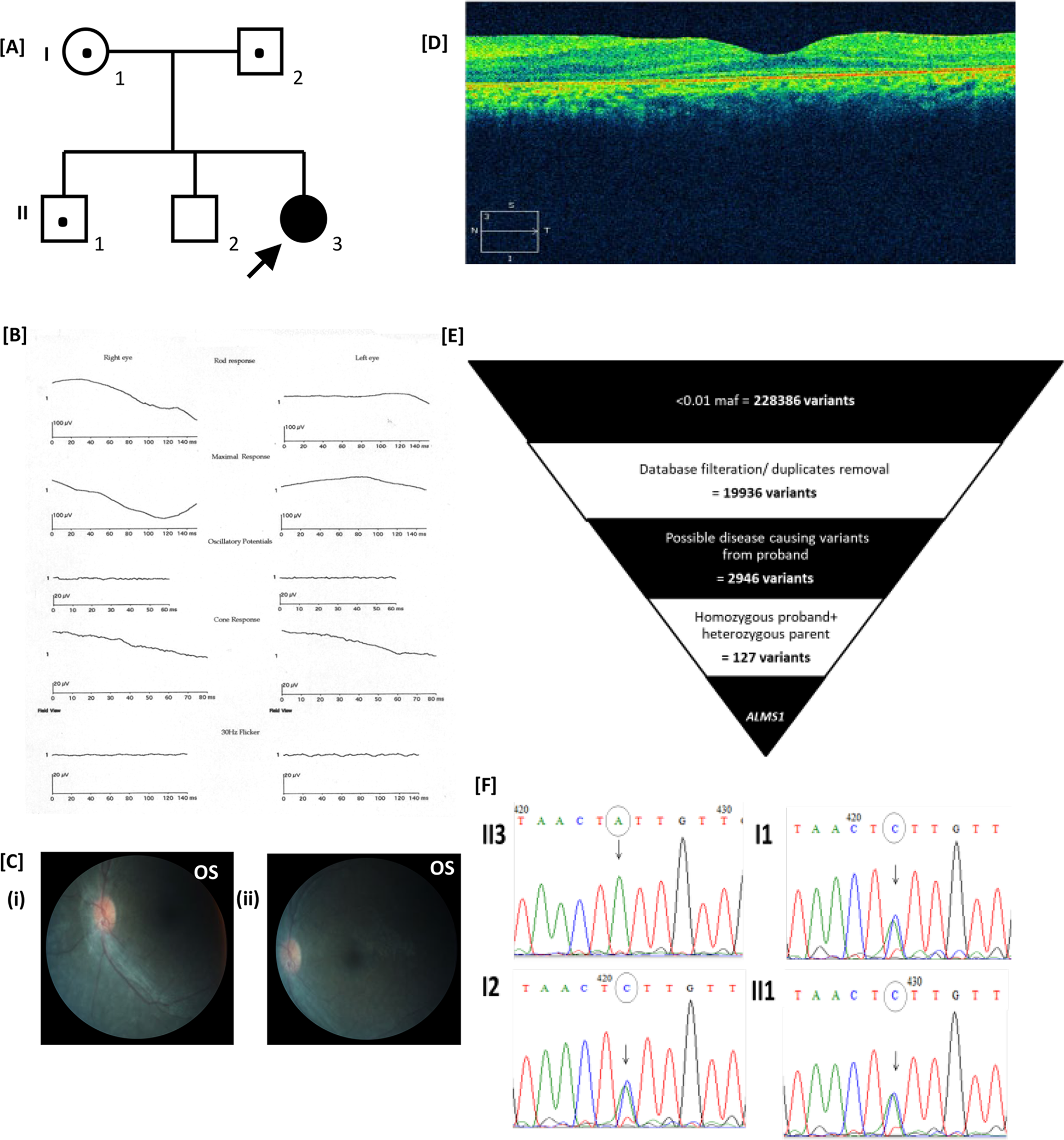
Whole-exome sequencing identifies two novel ALMS1 mutations in Indian patients with Leber congenital amaurosis
Recomendado para você
-
 Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome - Wikipedia12 abril 2025
Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome - Wikipedia12 abril 2025 -
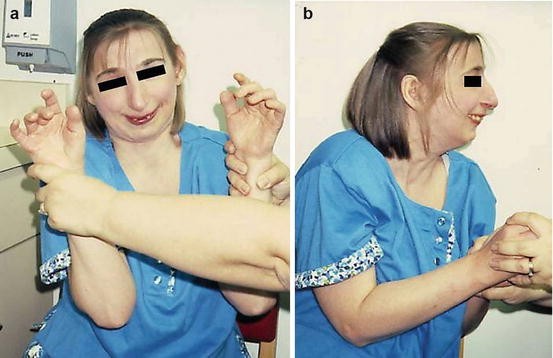 Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome12 abril 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome12 abril 2025 -
 Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf12 abril 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf12 abril 2025 -
![Figure 1. [Facial appearance of a girl age 11 years with FHS (SRCAP pathogenic variant p.Arg2444Ter)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK114458/bin/fhs-Image001.jpg) Figure 1. [Facial appearance of a girl age 11 years with FHS (SRCAP pathogenic variant p.Arg2444Ter)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf12 abril 2025
Figure 1. [Facial appearance of a girl age 11 years with FHS (SRCAP pathogenic variant p.Arg2444Ter)]. - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf12 abril 2025 -
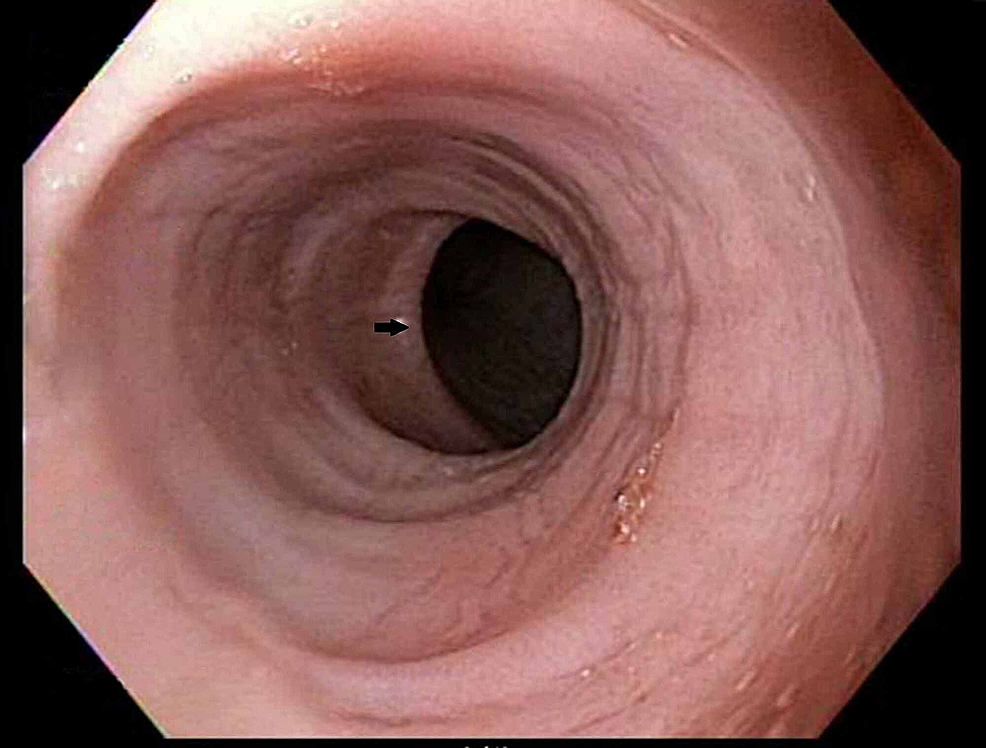 Cureus Barrett's Esophagus in Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome12 abril 2025
Cureus Barrett's Esophagus in Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome12 abril 2025 -
 PDF) Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: Dental manifestations and management12 abril 2025
PDF) Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: Dental manifestations and management12 abril 2025 -
 PDF) The behavioral phenotype of Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: A scoping review of the literature12 abril 2025
PDF) The behavioral phenotype of Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: A scoping review of the literature12 abril 2025 -
 Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf12 abril 2025
Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome - GeneReviews® - NCBI Bookshelf12 abril 2025 -
 Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: principal oral and dental disorders and literature update12 abril 2025
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: principal oral and dental disorders and literature update12 abril 2025 -
 PDF) Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly12 abril 2025
PDF) Identification of de novo EP300 and PLAU variants in a patient with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome-related arterial vasculopathy and skeletal anomaly12 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 FIFA poderá punir Neymar por promessa que fez a Bolsonaro12 abril 2025
FIFA poderá punir Neymar por promessa que fez a Bolsonaro12 abril 2025 -
 Justin Murphy (cath/acc) on X: TIL quirked up shawty / X12 abril 2025
Justin Murphy (cath/acc) on X: TIL quirked up shawty / X12 abril 2025 -
 Mahoutsukai Reimeiki revela video e mais detalhes sobre o anime12 abril 2025
Mahoutsukai Reimeiki revela video e mais detalhes sobre o anime12 abril 2025 -
 COMO DESENHAR A LULUCA NO PK XD12 abril 2025
COMO DESENHAR A LULUCA NO PK XD12 abril 2025 -
 Gotham Knights episode 11 recap: The identity of Duela finally12 abril 2025
Gotham Knights episode 11 recap: The identity of Duela finally12 abril 2025 -
 IS Infinite Stratos 2 Infinite Wedding Folder Icon by12 abril 2025
IS Infinite Stratos 2 Infinite Wedding Folder Icon by12 abril 2025 -
 Nintendo DS - Assassin's Creed II: Discovery12 abril 2025
Nintendo DS - Assassin's Creed II: Discovery12 abril 2025 -
 😮Curiosidades INCRÍVEIS sobre o Super Saiyajin 412 abril 2025
😮Curiosidades INCRÍVEIS sobre o Super Saiyajin 412 abril 2025 -
 Beyblade: Metal Fusion12 abril 2025
Beyblade: Metal Fusion12 abril 2025 -
 Pixie, Gacha Life Wiki12 abril 2025
Pixie, Gacha Life Wiki12 abril 2025