Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 02 abril 2025
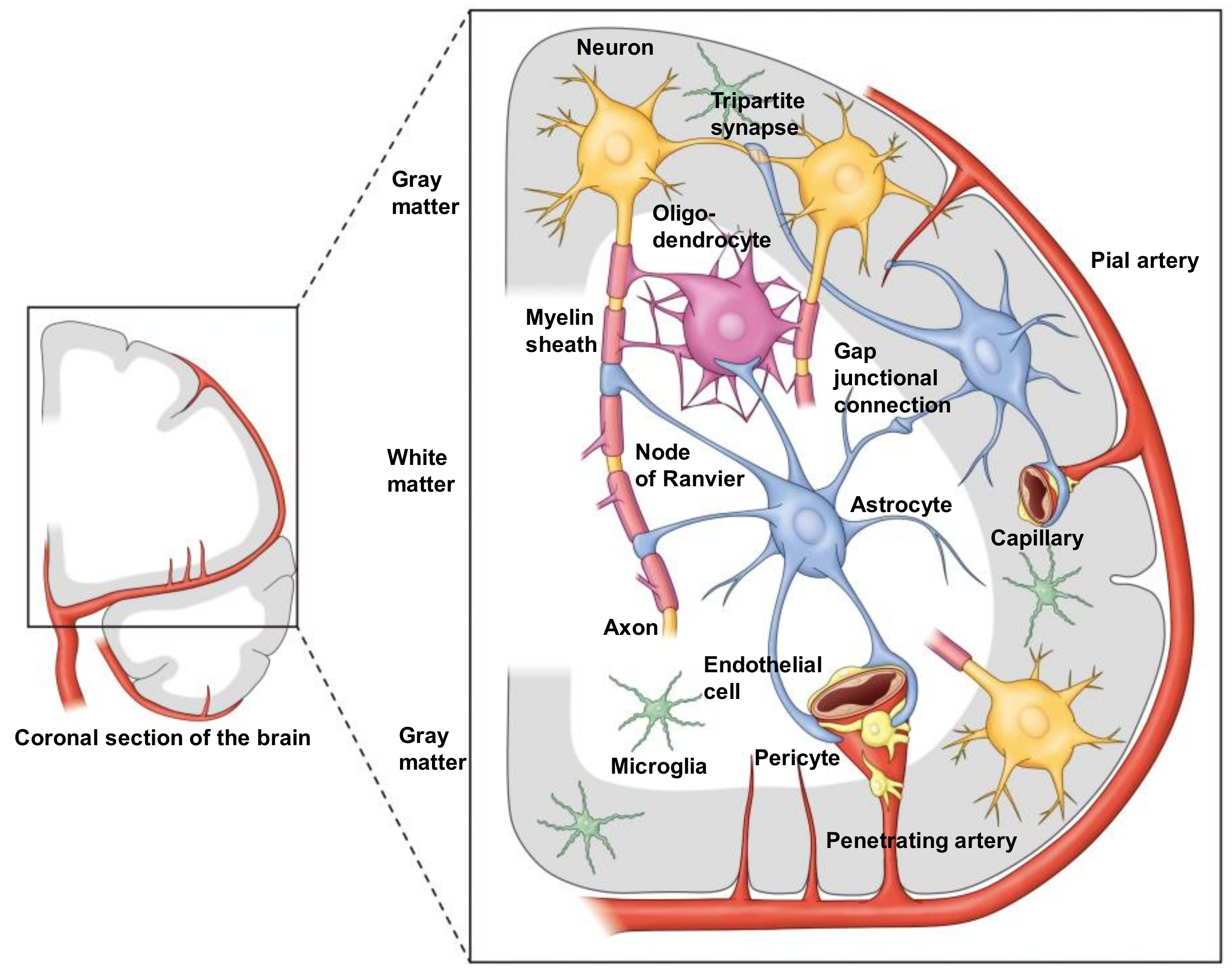
The neurovascular unit (NVU) is a conceptual framework that has been proposed to better explain the relationships between the neural cells and blood vessels in the human brain, focused mainly on the brain gray matter. The major components of the NVU are the neurons, astrocytes (astroglia), microvessels, pericytes, and microglia. In addition, we believe that oligodendrocytes should also be included as an indispensable component of the NVU in the white matter. Of all these components, astrocytes in particular have attracted the interest of researchers because of their unique anatomical location; these cells are interposed between the neurons and the microvessels of the brain. Their location suggests that astrocytes might regulate the cerebral blood flow (CBF) in response to neuronal activity, so as to ensure an adequate supply of glucose and oxygen to meet the metabolic demands of the neurons. In fact, the adult human brain, which accounts for only 2% of the entire body weight, consumes approximately 20–25% of the total amount of glucose and oxygen consumed by the whole body. The brain needs a continuous supply of these essential energy sources through the CBF, because there are practically no stores of glucose or oxygen in the brain; both acute and chronic cessation of CBF can adversely affect brain functions. In addition, another important putative function of the NVU is the elimination of heat and waste materials produced by neuronal activity. Recent evidence suggests that astrocytes play pivotal roles not only in supplying glucose, but also fatty acids and amino acids to neurons. Loss of astrocytic support can be expected to lead to malfunction of the NVU as a whole, which underlies numerous neurological disorders. In this review, we shall focus on historical and recent findings with regard to the metabolic contributions of astrocytes in the NVU.
IAPP/amylin-induced interaction between NLRP3 and ASC in a cell-free

Sequencing of Circulating Cell-free DNA during Pregnancy
JCM, Free Full-Text
Nt Novo Cella Get File - Colaboratory
The dependence of cell-free protein synthesis in E. coli upon naturally occurring or synthetic polyribonucleotides. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Sequencing of Circulating Cell-free DNA during Pregnancy

Effect of calendar ageing on the cycle life of anode-free full-cells.
Frontiers Combining Cell-Free Protein Synthesis and NMR Into a Tool to Study Capsid Assembly Modulation
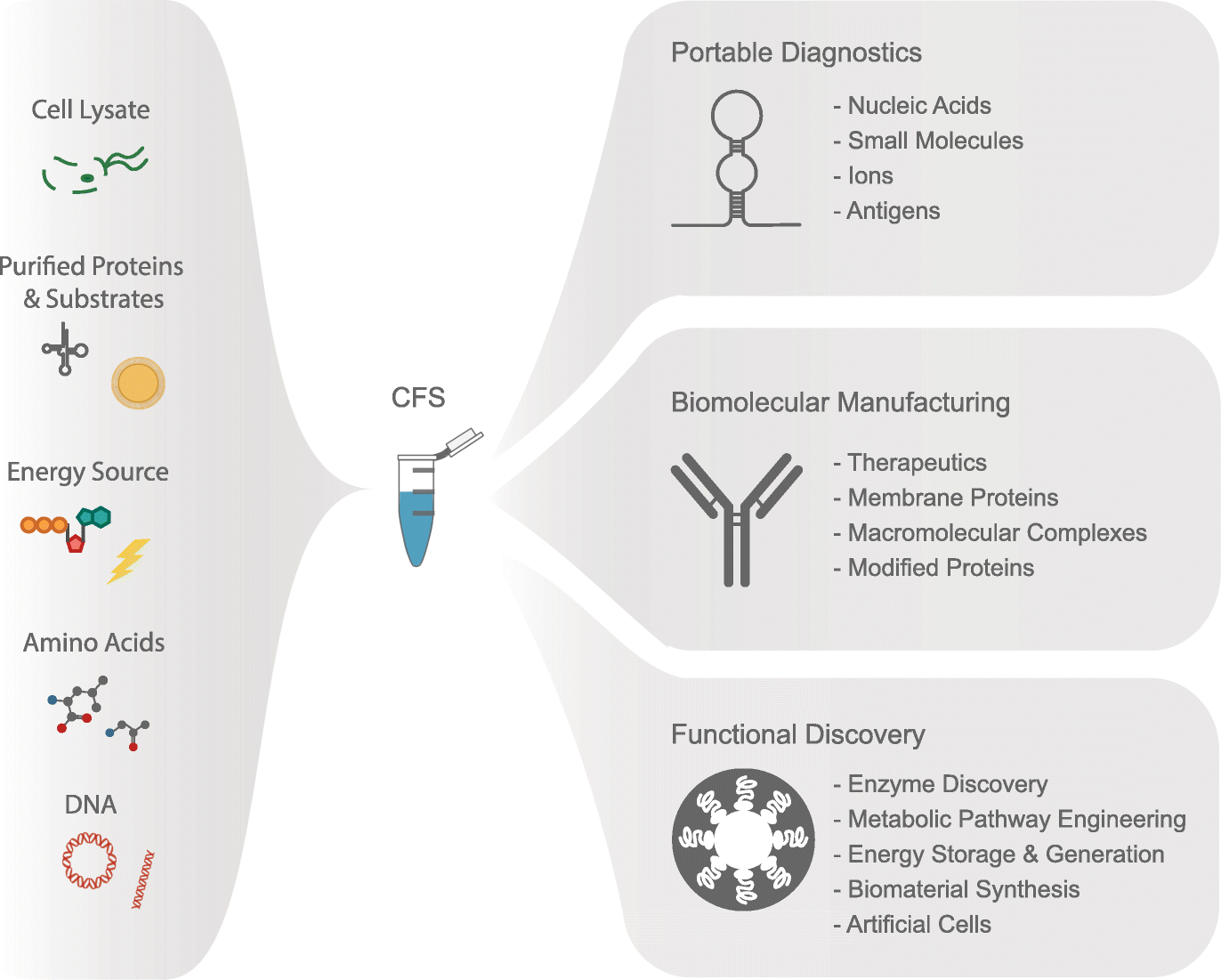
Cells, Free Full-Text
Recomendado para você
-
 Latino Leaders May - June by Latino Leaders - Issuu02 abril 2025
Latino Leaders May - June by Latino Leaders - Issuu02 abril 2025 -
 Adrian GARDA, Professor (Full), PhD in Zoology02 abril 2025
Adrian GARDA, Professor (Full), PhD in Zoology02 abril 2025 -
 Industrial trawl fishery for B. vaillantii. Trawl fisheries in the02 abril 2025
Industrial trawl fishery for B. vaillantii. Trawl fisheries in the02 abril 2025 -
 Staff (expert) Archives - The Dialogue02 abril 2025
Staff (expert) Archives - The Dialogue02 abril 2025 -
/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_59edd422c0c84a879bd37670ae4f538a/internal_photos/bs/2023/b/9/9mt5SLSlS0hTtomXz7hQ/coelho.jpg) Fim de semana em Campo Grande tem bazar de páscoa, feiras e02 abril 2025
Fim de semana em Campo Grande tem bazar de páscoa, feiras e02 abril 2025 -
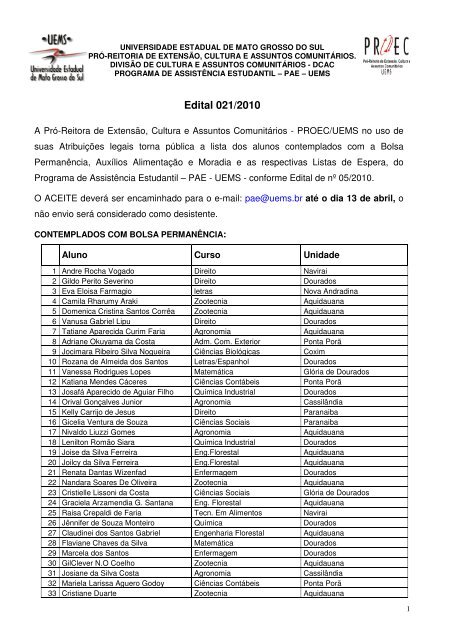 1. lista dos alunos contemplados com a Bolsa Permanência02 abril 2025
1. lista dos alunos contemplados com a Bolsa Permanência02 abril 2025 -
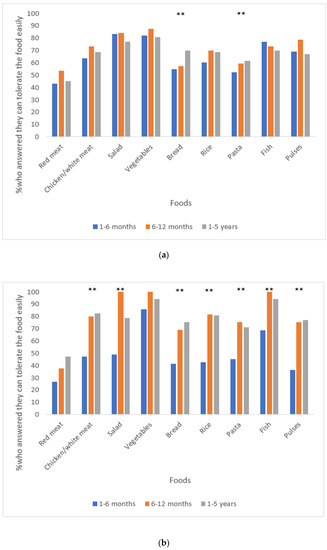 Nutrients, Free Full-Text02 abril 2025
Nutrients, Free Full-Text02 abril 2025 -
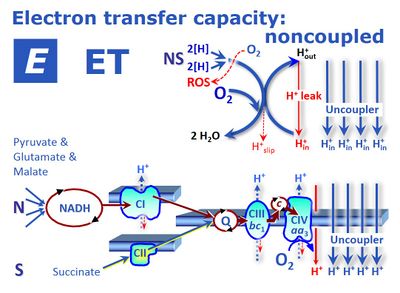 ET capacity - Bioblast02 abril 2025
ET capacity - Bioblast02 abril 2025 -
 CU Denver Fall Commencement 2022 by CU Denver - Issuu02 abril 2025
CU Denver Fall Commencement 2022 by CU Denver - Issuu02 abril 2025 -
 Editora CRV02 abril 2025
Editora CRV02 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Slytherin Costumes for Adults & Kids02 abril 2025
Slytherin Costumes for Adults & Kids02 abril 2025 -
 Cofle AM - Cofle02 abril 2025
Cofle AM - Cofle02 abril 2025 -
 Khloé Kardashian Accused Of Blackfishing Over Bratz Costume02 abril 2025
Khloé Kardashian Accused Of Blackfishing Over Bratz Costume02 abril 2025 -
 Is the Dead Space Remake coming to Xbox Game Pass? - Dexerto02 abril 2025
Is the Dead Space Remake coming to Xbox Game Pass? - Dexerto02 abril 2025 -
 Cooking Simulator (@cookingsim) / X02 abril 2025
Cooking Simulator (@cookingsim) / X02 abril 2025 -
 A new era for Five Nights at Freddy's: Security Breach – The02 abril 2025
A new era for Five Nights at Freddy's: Security Breach – The02 abril 2025 -
 Introducing the Legendary Bruce Lee in Hitori No Shita: The02 abril 2025
Introducing the Legendary Bruce Lee in Hitori No Shita: The02 abril 2025 -
 K-ON - Yui Hirasawa by DrawingWithRaymond on DeviantArt02 abril 2025
K-ON - Yui Hirasawa by DrawingWithRaymond on DeviantArt02 abril 2025 -
True Love - song and lyrics by ConKi, Barmuda02 abril 2025
-
 Castle Crashers Wiki, HD Png Download , Transparent Png Image02 abril 2025
Castle Crashers Wiki, HD Png Download , Transparent Png Image02 abril 2025
